Figure 55.
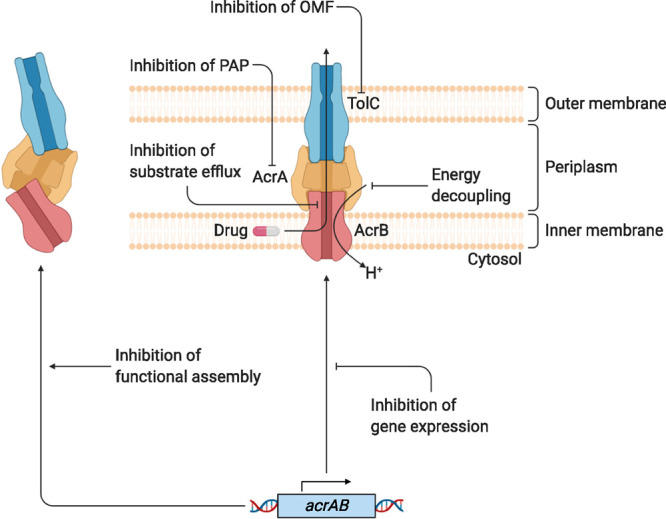
Schematic diagram of the different mechanisms of action of efflux inhibitors. Inhibition of gene expression prevents transcription of efflux genes, thereby reducing efflux pump expression. Compounds that inhibit the functional assembly work by interfering with the interaction surfaces between the components of the tripartite efflux systems. Energy decoupling agents facilitate flow of protons, thereby dissipating the electrochemical gradient, so that it cannot be exploited as an energy source by efflux pumps. Inhibitors of substrate efflux can work as a competitive inhibitor by actively competing with the binding site to prevent substrate binding or by blocking conformational change to prohibit enzymatic catalysis. Inhibitors of periplasmic adaptor proteins (PAP) are thought to work by preventing binding to the inner membrane transporter and by preventing self-association of the PAP protomers. Outer membrane factor (OMF) inhibitors block the periplasmic entrance site to prevent translocation of substrates across the outer membrane. PAP, periplasmic adaptor protein; OMF, outer membrane factor.
