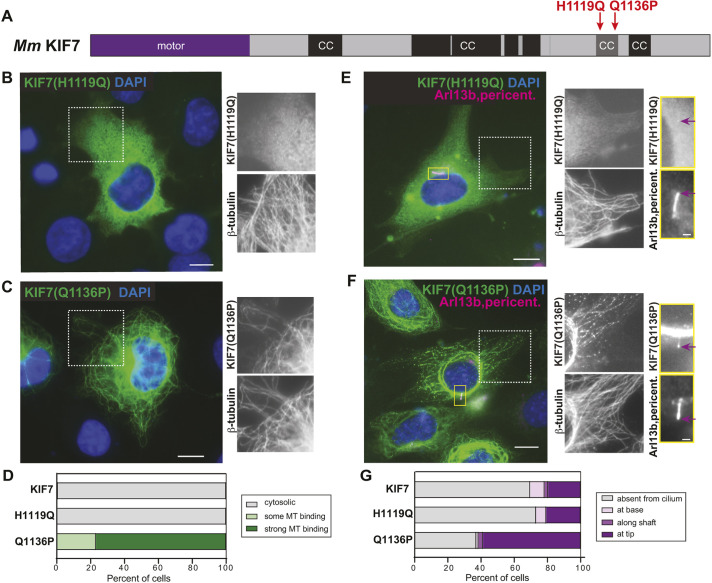
Fig. 4.
The disease-associated mutation Q1136P in the inhCC relieves auto-inhibition. (A) Domain organization of full-length KIF7. The positions of the disease-associated mutations H1119Q and Q1136P are indicated on top. CC, coiled coil; black box, CC prediction >90%; gray box, CC prediction >80%, according to COILS software. (B-D) COS-7 cells expressing mCit-tagged H1119Q (B) or Q1136P (C) mutant versions of KIF7 were fixed and stained with an antibody against β-tubulin to mark microtubules (MT) and with DAPI to mark the nucleus. The white boxed region is shown to the right with separated channels for KIF7-mCit and microtubules. (D) Quantification of microtubule binding. n=136 (KIF7), 223 [KIF7(H1119Q)] and 177 [KIF7(Q1136P)] cells across at least three independent experiments. (E-G) NIH-3T3 cells expressing mCit-tagged H1119Q (E) or Q1136P (F) mutant versions of KIF7 were fixed and stained with antibodies against β-tubulin to mark microtubules, Arl13b to mark the primary cilium, pericentrin to mark the basal body and DAPI to mark the nucleus. The white boxed region is shown to the right with separate images of KIF7-mCit and microtubules. The primary cilium in the yellow boxed region is shown to the far right with separate images of KIF7 and the cilium markers. Purple arrows indicate localization at the cilium tip. (G) Quantification of cilium localization. n=46 (KIF7), 82 [KIF7(H1119Q)] and 78 [KIF7(Q1136P)] cells across at least three independent experiments. Scale bars: 10 µm (B,C,E,F); 1 µm (E,F, far right panels).