Figure 2.
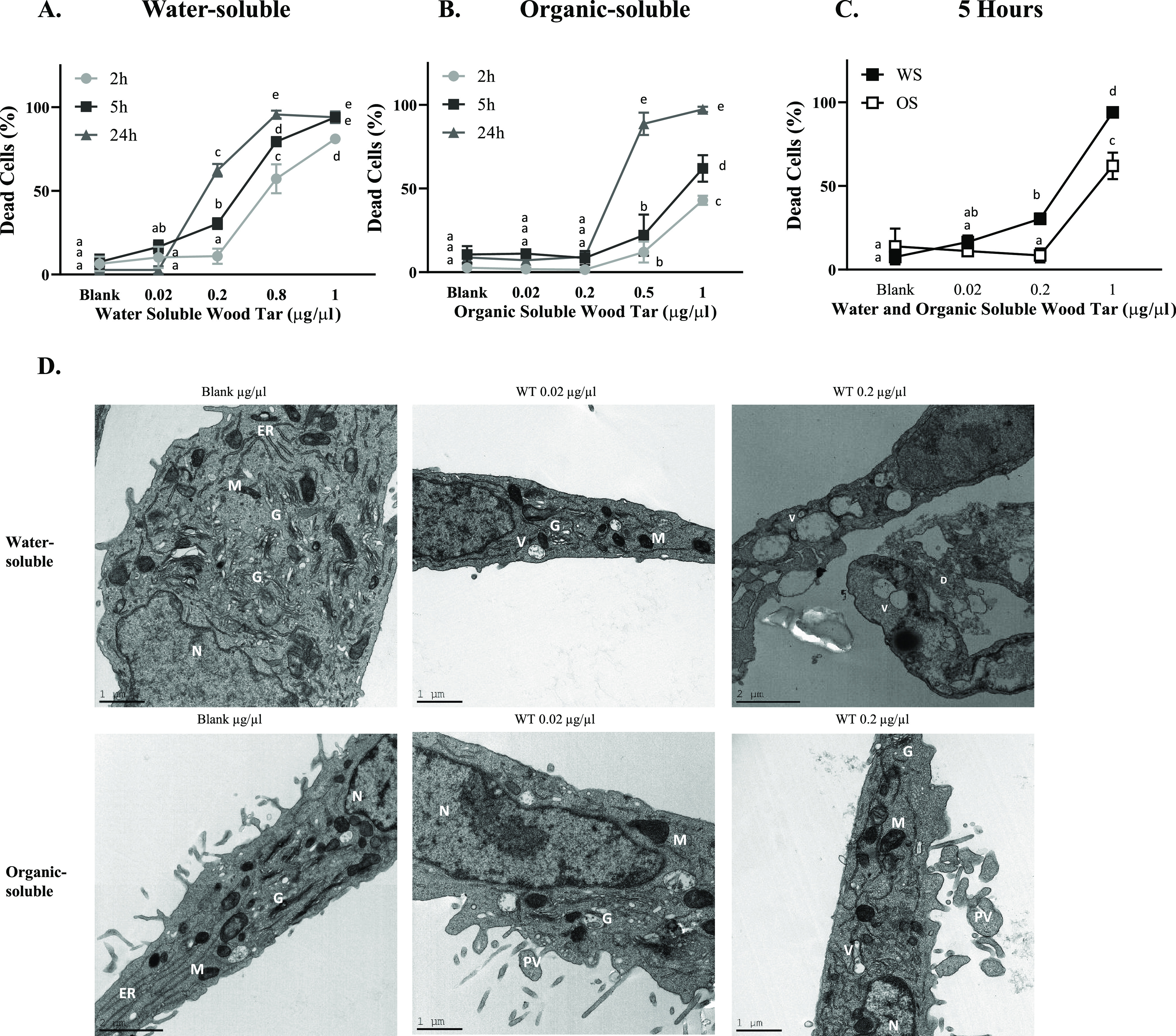
Wood tar extracts induced cell death in A549 lung epithelial cells. Lung epithelial cells were exposed to (A) water-soluble (WS) or (B) organic-soluble (OS) wood tar extracts at concentrations of 0.02, 0.2, or 1 mg/mL for the indicated times (2, 5, and 24 h). Cell cytotoxicity was determined by the intercalating PI dye. (C) Cell toxicity after 5 h of exposure to both water-soluble and organic-soluble wood tar extracts. The data represent the mean ± SD. Means with different letters are significantly different at p < 0.05 using the Tukey HSD test. These experiments were performed in triplicate and were repeated twice. (D) TEM images of control (blank treated, water-soluble and organic-soluble) cells, 0.02 mg/mL water-soluble and organic-soluble wood tar extract-treated cells, and 0.2 mg/mL water-soluble and organic-soluble wood tar extract-treated cells after 5 h of exposure. M, mitochondria; N, nucleus; V, vacuoles; D, dead cell; PV, phagocytic vesicles, G; Golgi apparatus.
