Figure 7. Model for cScap Conformational Changes.
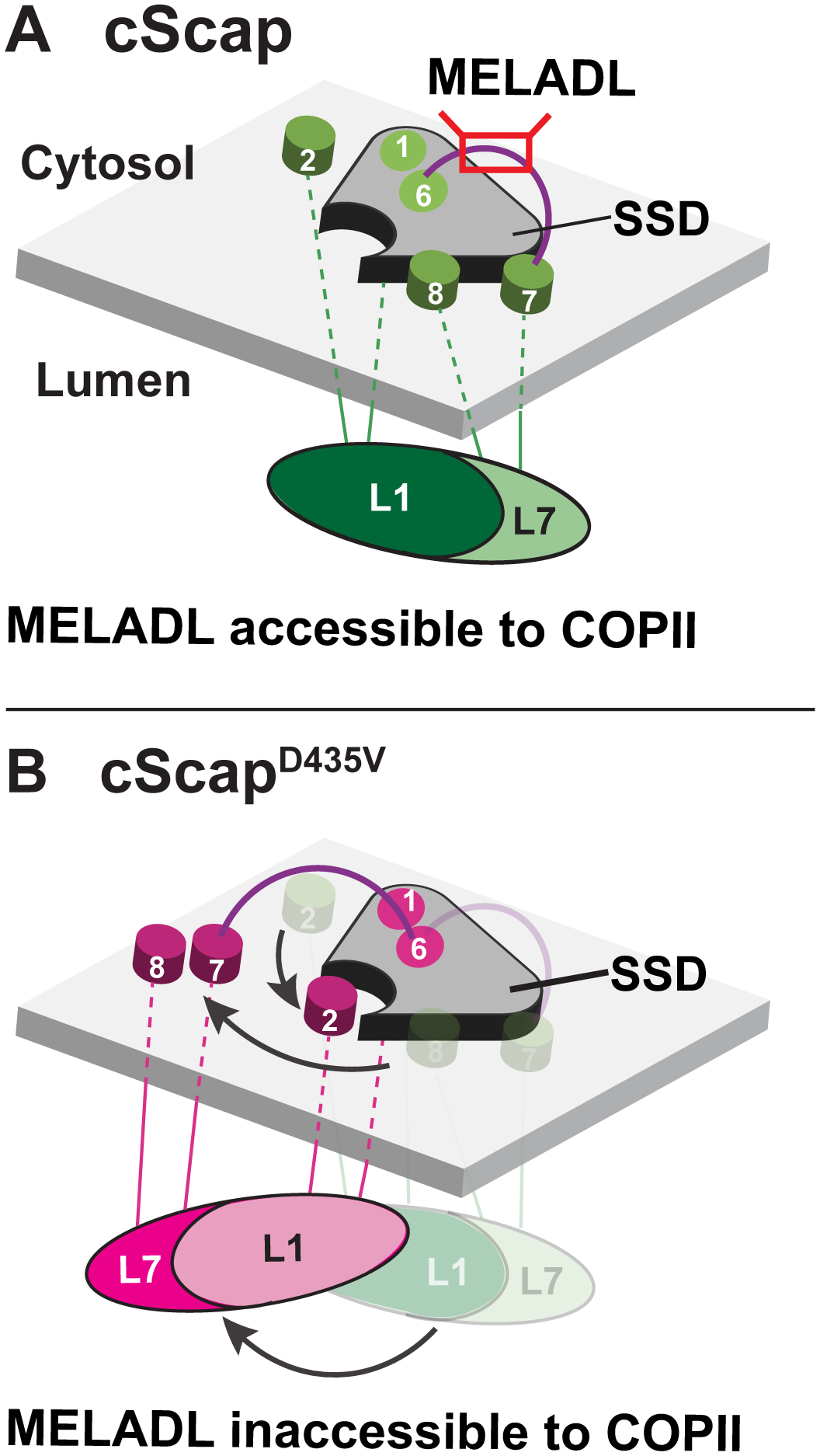
(A) When cScap is free from cInsig-1, the L1-L7 domain is positioned directly underneath the SSD module and the TM7-TM8 module is bound to the SSD. In this conformation, the MELADL sequence on the cytoplasmic loop connecting TM6 and TM7 is accessible to COPII proteins.
(B) In the cInsig-1 bound form triggered by mutation of cScap’s D435 to V, the L1-L7 domain rotates away from the cScap SSD module. For clarity, cInsig-1 is not shown. The rotation of the L1-L7 domain moves TM2 into position to create a binding interface for Insig-1 as shown in Figure 6B. Moreover, the TM7-TM8 module is moved away from the SSD to provide Insig-1 access to this interface. These conformational changes on the luminal side may cause a concerted change in MELADL-containing L6 on the cytoplasmic side to prevent interactions with COPII proteins.
See also Figure S7.
