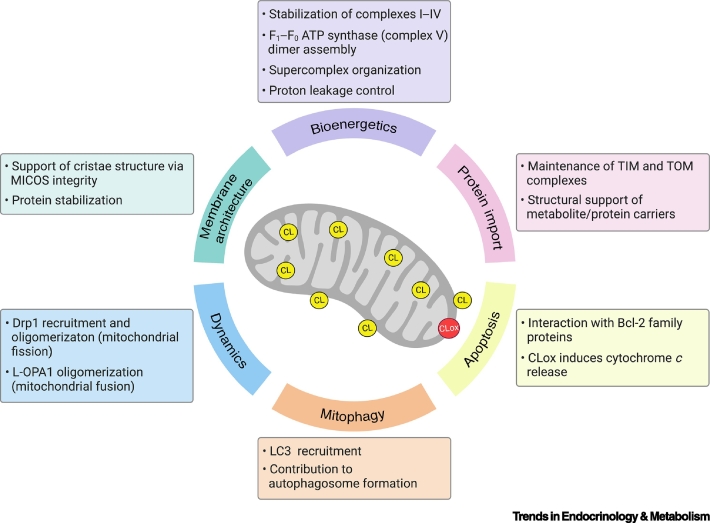
Figure 2.
Roles of Cardiolipin (CL) in Mitochondria.
CL is primarily localized within the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), where it contributes to maintenance of mitochondrial membrane architecture, bioenergetics, and the stability of protein carriers. In the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), a small fraction of CL serves as a signaling molecule for selective elimination of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy. CL is also an essential mediator of apoptosis through two mechanisms involving cytochrome c release that is triggered by CL peroxidation and externalization, and binding to Bcl-2 family protein Bid to induce Bax and Bak oligomerization. Finally, CL in the OMM and IMM regulates mitochondrial fission and fusion dynamics. Figure partially created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: Bak, Bcl-2 antagonist/killer1; Bax, Bcl-2 associated X protein; Bid, BH3 interacting domain death agonist; CDP-DAG, cytidine diphosphate-diacylglycerol; CLox, oxidized cardiolipin; Drp1, dynamin-related protein 1; L-OPA1, long isoforms of optic atrophy 1; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; MICOS, mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system; TIM, translocase of the inner membrane; TOM, translocase of the outer membrane.