Fig. 5. ExoT/ADPRT-induced G1 cell cycle arrest in melanoma cells likely involves Crk.
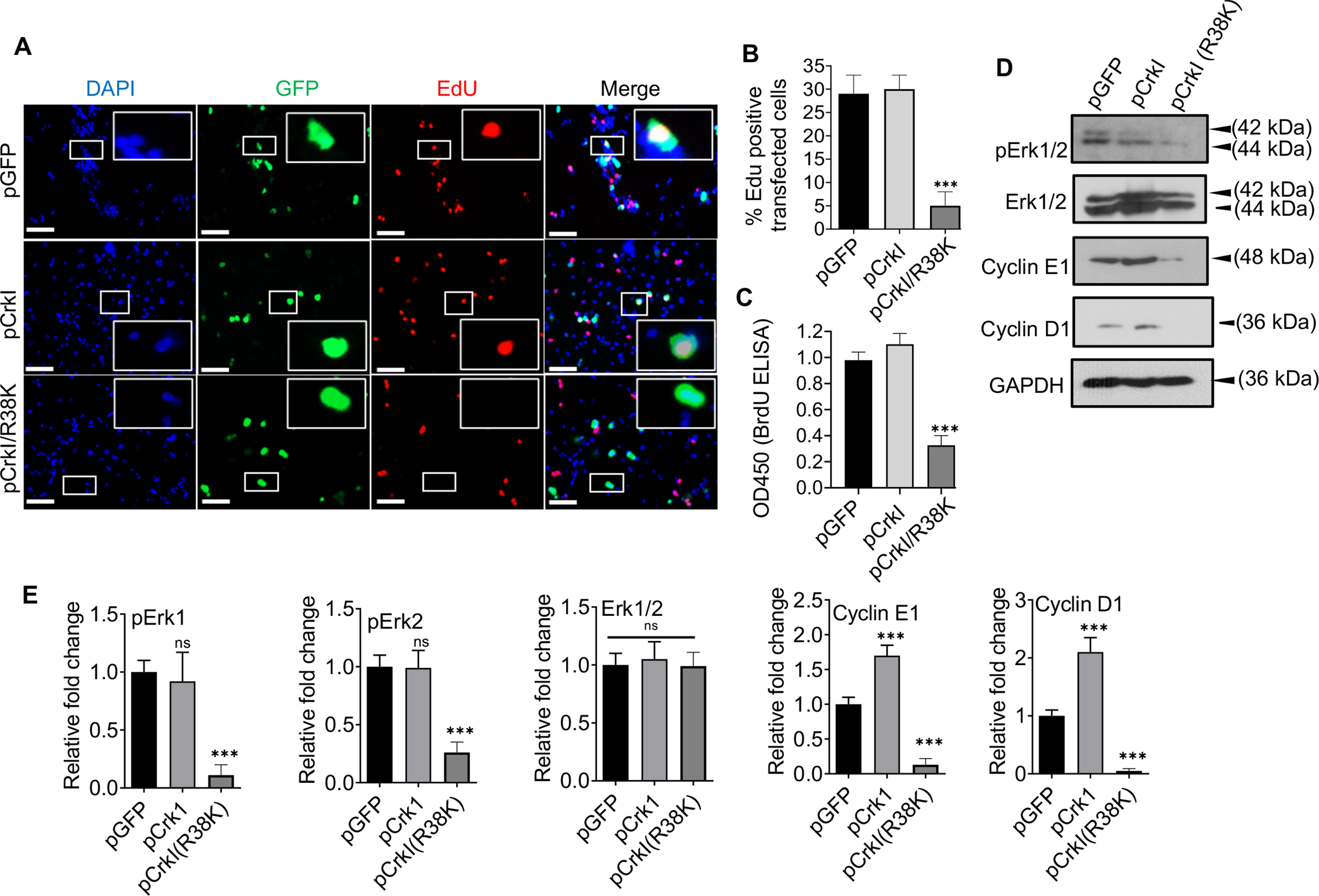
A-B) B16 cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors in the presence of Z-VAD. Cell cycle arrest in G1 in transfected cells (green) was determined, using EdU DNA incorporation (red), by IF microscopy, 48h after transfection. DAPI was used to stain nucleus (blue). Representative images are shown. Inserts are the magnified images of representative cells. The scale bar is 20μM. B) The tabulated results of (A) are shown as the Mean ± SEM. (N=3, ***p<0.001; One-way ANOVA). C) B16 were transfected with indicated expression vectors in the presence of Z-VAD. Cell cycle arrest in G1 was determined by BrdU Cell Proliferation ELISA Kit, 48h after transfection (N=3; ns, not significant, *** p<0.001; One-way ANOVA). D) B16 were transfected with indicated expression vectors in the presence of Z-VAD. Cell lysates were collected 48h after transfection and assessed for the indicated G1/S checkpoint proteins by Western blotting. (E) the corresponding densitometer data from 3 replicates, as compared to pGFP control vector, are shown, after normalizing the data with their corresponding GAPDH levels. (N=3; ns, not significant, *** p<0.001; One-way ANOVA).
