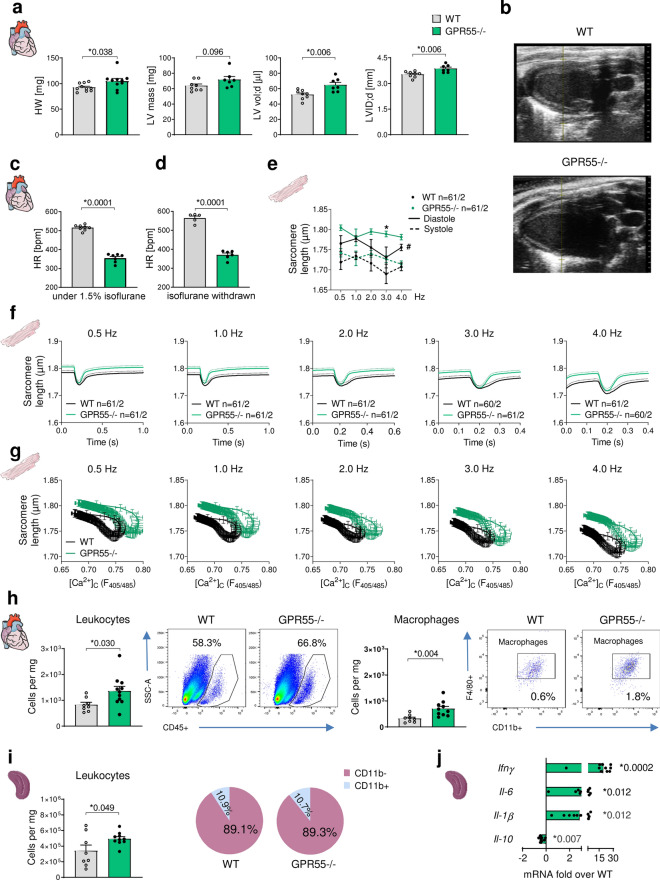
Figure 1.
Baseline characterization of GPR55 deficient mice. (a) Basal cardiac phenotype of WT and GPR55−/− mice, aged 8 weeks, as determined by gravimetry and echocardiography (n = 8–11/group). (b) Representative echocardiographic B-Mode projections of WT and GPR55−/− hearts. Basal heart rate of WT and GPR55−/− mice (c) under 1.5% isoflurane inhalation (n = 7–8/group) and (d) under conscious conditions upon isoflurane withdrawal (n = 5–6/group). (e) Sarcomere length in isolated WT and GPR55−/− cardiomyocytes during diastole (solid lines) and systole (dotted lines) under increasing pacing frequencies. Circles indicate mean ± SE; #p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (*p < 0.05 vs. WT); n indicates number of isolated cardiomyocytes from 2 mice. (f) Sarcomere length recordings from isolated WT and GPR55−/− cardiomyocytes under increasing pacing frequencies over time. Solid lines indicate mean + SE (dotted line). (g) Ca2+ dependent sarcomere length in WT and GPR55−/− cardiomyocytes. (h) Basal LV leukocyte counts and herein macrophage numbers in WT and GPR55−/− mice detected via flow cytometry, and representative dot plots indicating respective leukocyte (CD45+) and macrophage (CD11b+ F4/80+) counts as percentage of single cells (n = 8–12/group). (i) Basal splenic leukocyte counts and relative distribution of myeloid (CD11b+) and lymphoid (CD11b-) cells in WT and GPR55−/− mice detected via flow cytometry (n = 8–12/group). (j) Basal splenic chemokine gene expression in GPR55−/− mice as fold over WT (n = 8–12/group). Bars and squares indicate mean ± SE (Comparison between two groups: Student’s t-test).