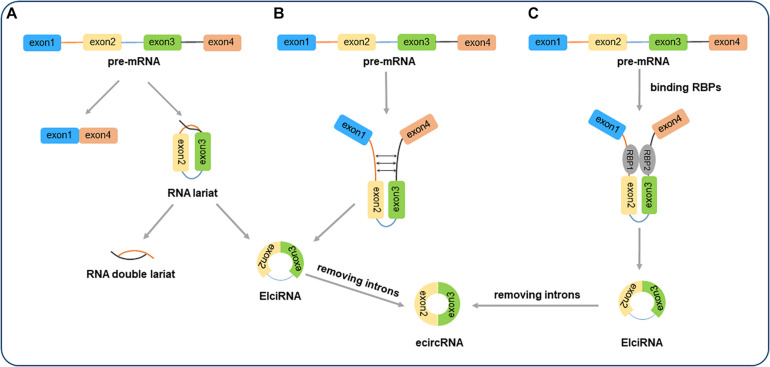
FIGURE 1.
The biogenesis of circular RNAs (circRNAs). (A) Lariat-driven circularization. EIciRNAs or ecircRNAs are generated by exon skipping. The 3′splice site is attacked by exons 5′, forming an mRNA composing of exon 1 and exon 4 and an RNA lariat embodying skipped exon 2 and exon 3. Then, an RNA double lariat and an EIciRNA were further generated. (B) Intron-pairing-driven circularization. The pairing of the inverted complementary sequences in the flanking introns makes the splicing sites close to each other, promoting the circularization of intervening exons. And EIciRNAs or ecircRNAs are formed by retaining or removing introns. (C) RNA-binding protein (RBP)-driven circularization. RBPs binding to the flanking introns, which act as a bridge to make flanking introns close to each other, facilitating the process of circularization.