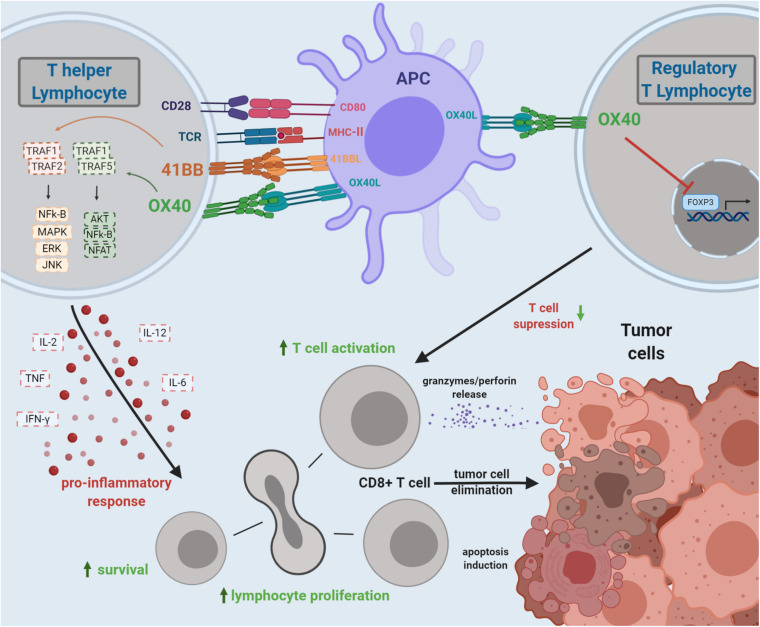
FIGURE 1.
Costimulation by 4-1BB and OX40 TCRs and the overall effects on antitumor T-cell immunity. 4-1BB and OX40 bind to their ligands, triggering a signaling cascade leading to T-cell activation and expansion of cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes. Costimulation of OX40 may also inhibit the FOXP3 transcription factor on CD4+ T cells, impairing the Treg function, diminishing tumor immunosuppression, and boosting the antitumor immune response. The 4-1BB/4-1BBL signaling triggers biochemical signals that increase TH1 cytokines and suppress TH2 cytokines; potentiate activation, survival, proliferation, and cytotoxicity of T cells; and provoke the maturation of dendritic cells. The OX40/OX40L interaction triggers a signaling cascade, similar to 4-1BB/4-1BBL, inducing transcriptional changes to modulate the immune response. The OX40 costimulation may promote T-cell proliferation and survival. The agonistic signaling transduced by OX40 on Treg may impair FOXP3 expression, enhancing antitumor response.