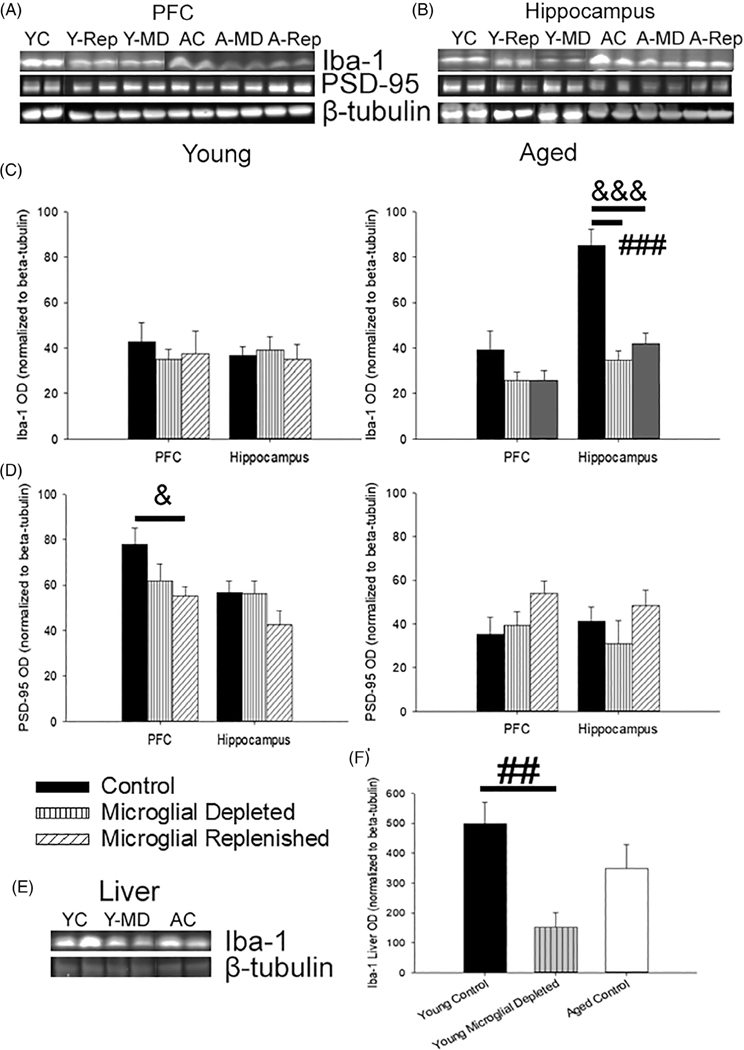
FIGURE 2.
PLX3397 treatment reduced Iba-1 expression in the brain and liver and shifted synaptic and astrocytic markers. (a,b) Representative images of immunoblots examining changes in microglial and synaptic protein markers in the PFC and hippocampus following microglial depletion and replenishment (5–9 young rats/treatment; 4–7 aged rats/treatment). (c) Levels of hippocampal Iba-1 decreased with microglial depletion and replenishment in aged animals. (d) Corresponding shifts in postsynaptic dynamics, measured by PSD-95, were examined. Age-related declines in PSD-95 were noted (p <.001); though within young rats, PLX3397 treatment tended to decrease prefrontal PSD-95 levels (p = .09), which failed to recover with microglial replenishment (p = .03). To examine off-site effects of PLX3397 treatment, liver Iba-1 levels were measured (e) and found to significantly decrease from microglial depletion within young (f), demonstrating an impact of PLX3397 treatment on both the brain and periphery. All data are represented as means ± SEM. ## p ≤.01, ### p ≤.001, control versus microglial depleted; & p ≤.05, &&& p ≤.001, control versus microglial replenished; ** p ≤.01, microglial depleted versus microglial replenished