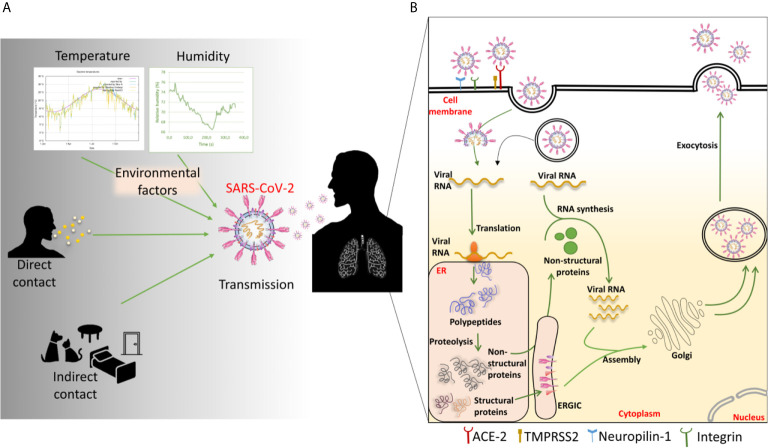
Figure 4.
(A) Factors involved in SARS-CoV-2 transmission and (B) mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cell. The transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs through various direct and indirect routes. Environmental factors like temperature and humidity show the impact on the transmission. Once the virus enters inside the host, it enters into the cell through angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2). It can also use various other cell surface receptors like neuropilin-1 to facilitate the entry and infectivity. By the membrane fusion or endosomal pathway, the virus releases its genetic material inside the cytoplasm. The viral RNA then gets transcribed and translated into polypeptides. The polypeptides are cleaved to generate various structural and non-structural proteins (nsps). The nsps help in viral replication and transcription. The more viral RNA copies are produced through the replication. Meanwhile, the structural proteins like E, M, and S proteins get embedded in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and transported to Golgi through ER-Golgi intermediate complex (ERGIC). The multiple numbers of new virions are then assembled and exocytosed of the cell to infect nearby cells.