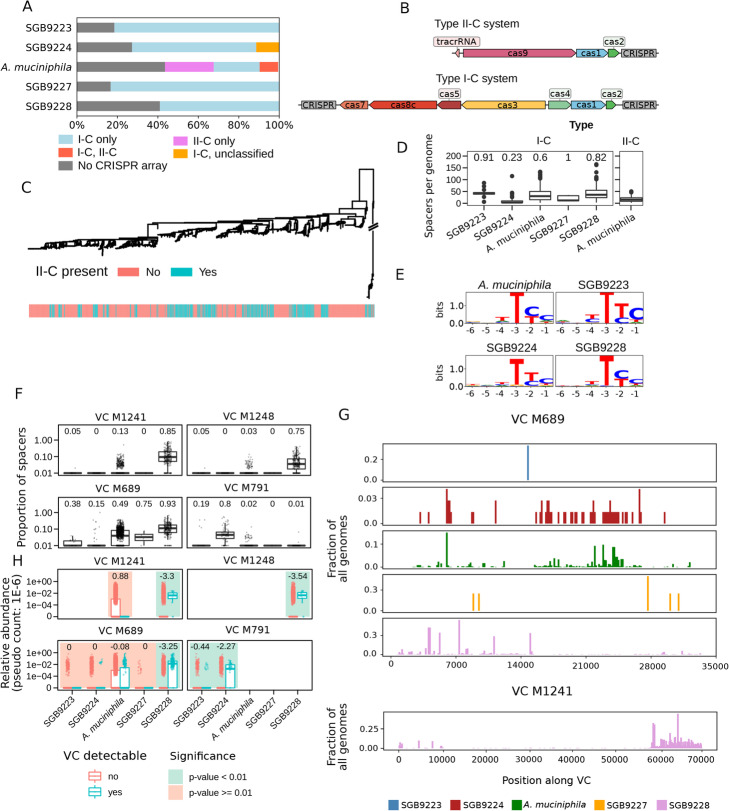
Fig. 3.
The CRISPR-Cas system of Akkermansia candidate species and their viral targets. A CRISPR locus type composition of Akkermansia candidate species. All candidate species possess CRISPR locus type I-C, with the exception of A. muciniphila in which type II-C is present in more than 30% of the genomes. B Representative locus organization of CRISPR loci over Akkermansia candidate species. Some type I-C loci contain only one CRISPR array. Gene and CRISPR array lengths are scaled to correspond to the median length over all loci. C Phylogenetic tree of A. muciniphila subspecies colored by type II-C presence. D The total number of spacer sequences for the genomes in each Akkermansia candidate species. Type II-C loci were only found in A. muciniphila. Numbers above the boxplots correspond to the fraction of type I-C loci with two CRISPR arrays. E Logo plots of predicted PAM sequences in putative (phage) Viral Clusters (VCs, see the “Methods” section) upstream of sequences with perfect matches against CRISPR spacer sequences from type I-C loci. F Proportion of CRISPR spacers within candidate species genomes with a near-perfect match (at most 2 mismatched nucleotides) for four VCs. The number above the box plots corresponds to the fraction of genomes with at least one spacer hit against a given VC (see the “Methods” section). G Mapping of spacers from Akkermansia genomes against two representative VCs, visualized with a sliding window of 150 nt. See Additional file 2: Figure S8 for the remaining VCs. H Distribution of the relative abundances of the Akkermansia candidate species based on the presence or absence of each cognate VC in the metagenome (Additional file 1: Table S2, see the “Methods” section). P-values for differential abundance were determined via two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. P-values of <0.01 were considered significant. The numbers above the box plots correspond to the generalized fold change, with negative numbers indicating a higher bacterial abundance when a VC is detected [60]