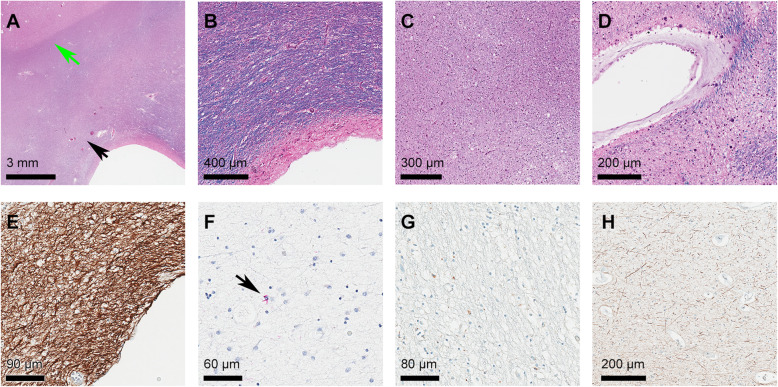
Fig. 3.
Selected examples of neuropathological findings in area of maximal white matter hyperintensity. A H&E/LFB staining of an FTLD-TDP case showing moderate (2) pallor of myelin staining within periventricular white matter (black arrow) in comparison to subcortical U fibers (green arrow); B H&E/LFB staining of an FTLD-tau (Pick’s) case showing pallor of periventricular myelin staining; C H&E/LFB staining of FTLD-tau (PSP) case showing severe myelin pallor; D H&E/LFB staining of an FTLD-tau (CBD) case showing collagenosis of large caliber periventricular veins; E GFAP immunolabeling of an FTLD-TDP case showing severe gliosis; F tau (AT8) immunohistochemistry of an FTLD-tau (CBD) case showing rare glial cytoplasmic tau immunopositive inclusions within the white matter region of interest (black arrow); G CD68 immunostaining of an FTLD-tau (Pick’s) case showing mild macrophage infiltration; H NF staining of an FTLD-tau (CBD) case showing severe axonal loss. Abbreviations: AD Alzheimer’s disease, CAA congophilic amyloid angiopathy, CBD corticobasal degeneration, CD68 cluster of differentiation 68, FTLD frontotemporal lobar degeneration, GFAP glial fibrillary acid protein, H&E/LFB Hematoxylin Eosin with Luxol Fast Blue, NF neurofilament, PSP progressive supranuclear palsy