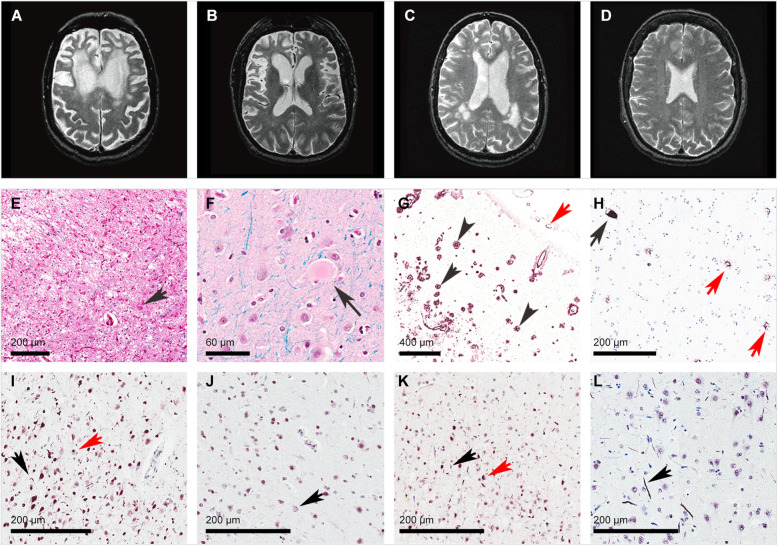
Fig. 4.
Selected examples of T2-weighted axial images and neurodegenerative neuropathological findings of participants. A T2-MRI of FTLD-TDP case with severe burden of WMH and prominent atrophy in medial and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex bilaterally; B T2-MRI of FTLD-tau (Pick's) case with prominent atrophy in medial and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex bilaterally with little WMH; C T2-MRI of AD case with WMH in posterior regions; and D T2-MRI of a healthy control. E H&E staining of FTLD-tau (Pick’s) case showing severe neuronal loss and gliosis in the frontal cortex with a ballooned neuron (black arrow); F H&E staining of FTLD-tau (CBD) case showing a ballooned neuron (black arrow) in frontal cortex; G beta-amyloid immunostaining of AD case showing frequent neuritic amyloid plaques (black arrows) and amyloid angiopathy (red arrow) in frontal cortex; and H tau (AT8) immunostaining of FTLD-tau (PSP) case showing a neurofibrillary tangle (black arrow) and astrocytic inclusions (red arrows). I FTLD-TDP Harmonized type A with short dystrophic neurites (black arrow) and compact neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (red arrow) preferentially located in superficial cortical layers. J FTLD-TDP Harmonized type B with diffuse granular neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (black arrow). K Mixed FTLD-TDP Harmonized A+B type with superficial dystrophic neurites (black arrow) and compact neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (red arrow). L FTLD-TDP Harmonized type C with long thick dystrophic neurites (black arrow). Abbreviations: AD Alzheimer’s disease, CBD corticobasal degeneration, FTLD frontotemporal lobar degeneration, PSP progressive supranuclear palsy