Fig. 3. Interactions of Dot1 with H2BUb and the acidic patch.
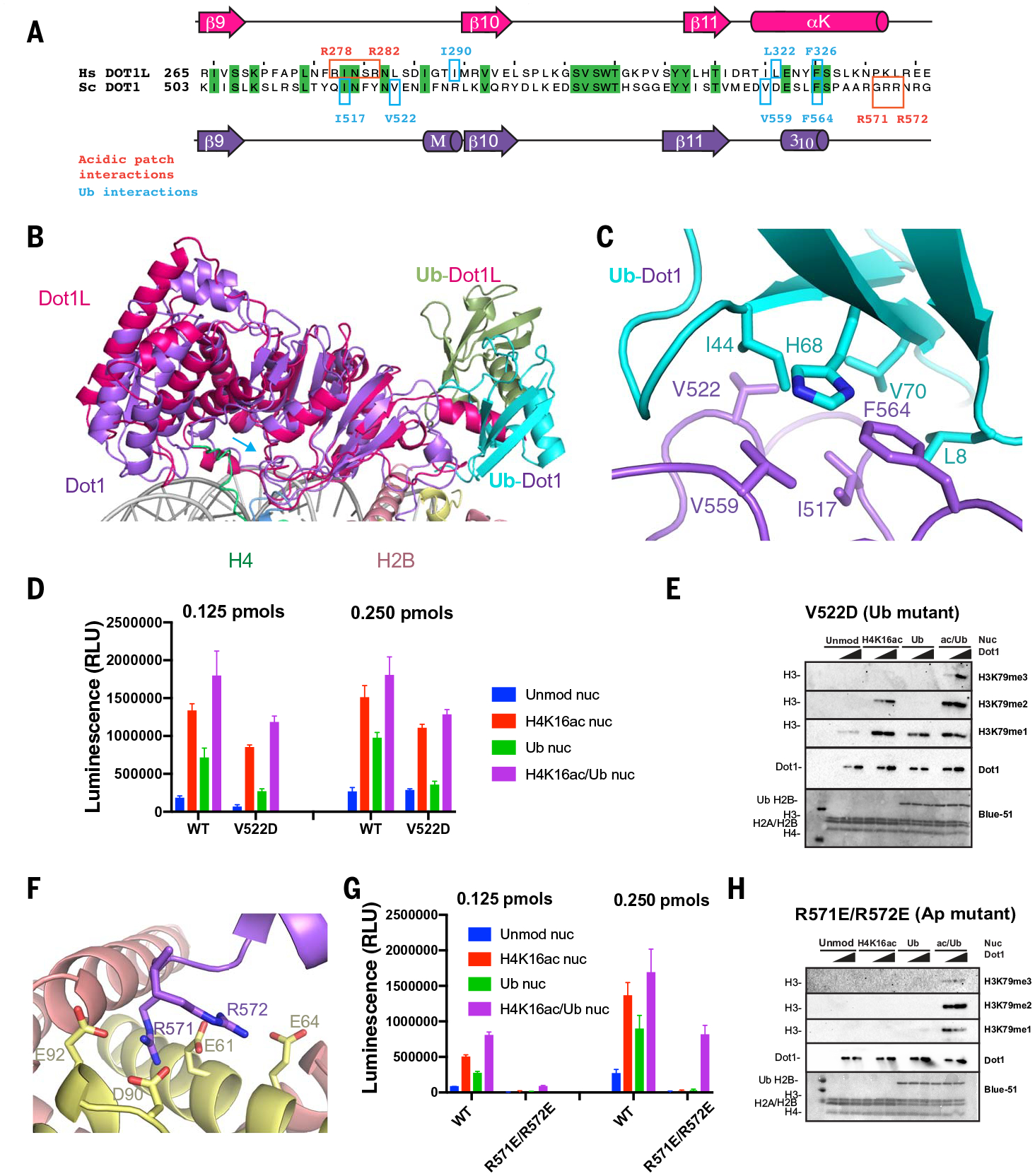
(A) Sequence alignment of budding yeast Dot1 (purple) and human Dot1L (red) showing primary and secondary structure of the catalytic domain and residues interacting with the ubiquitin (cyan) and the acidic patch (red). (B) Superposition of yeast Dot1 (purple) and Dot1L (red) [PDB ID 6NJ9 (40)] nucleosome structures showing the different surface of interaction with ubiquitin (shown in cyan in the yeast Dot1 structure and in green in the Dot1L structure). (C) Detailed view of interactions between Dot1 (purple) and ubiquitin (cyan). (D) Representative endpoint methyltransferase assay for Dot1 and V522D mutant in the presence of Unmod nuc or H4K16ac nuc or Ub nuc or ac/Ub nuc substrates. Reactions were performed with 0.125 and 0.250 pmol of Dot1. Each data point and error bar indicate the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (E) Representative HMT assay measuring activity of Dot1 and V522D mutant on different nucleosome substrates. HMT were performed with an increasing amount of Dot1 mutant (V522D) in the presence of Unmod nuc or H4K16ac nuc or Ub nuc or ac/Ub nuc substrates, and reaction products were identified by using Western blot. (F) Detailed view of interactions between Dot1 (purple) and nucleosome acidic patch (H2A, yellow; H2B, red). (G) Representative endpoint methyltransferase assay for Dot1 and (R571E-R572E) mutant in the presence of Unmod nuc or H4K16ac nuc or Ub nuc or ac/Ub nuc substrates. Reactions were performed with 0.125 pmol and 0.250 pmol of Dot1. Each data point and error bar indicate the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (H) Representative HMT assay measuring activity of Dot1 and mutant on different nucleosome substrates. HMT assays were performed with an increasing amount of Dot1 mutant (R571E-R572E) in the presence of Unmod nuc, H4K16ac nuc, Ub nuc, or ac/Ub nuc substrates, and reaction products were identified by using Western blot.
