Box 2 Figure:
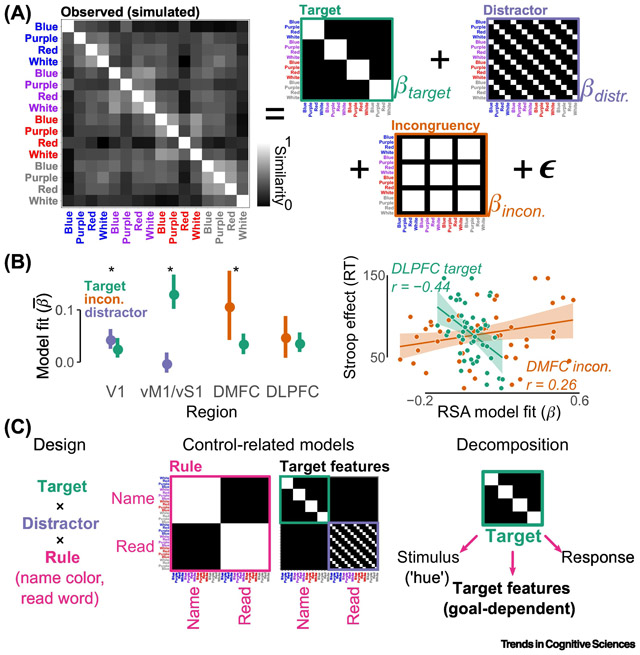
A decomposition of color-word Stroop via full factorial RSA. A, The similarity structure evoked during a Stroop experiment is modeled as a weighted sum of three hypothesized coding schemes (for visibility, white-hued stimuli are displayed in grey). B, Predicted dissociations in coding schemes were found when applying this approach to fMRI data [58]. At the group level (left), target coding predominated in ventral somatomotor cortex (vM1/vS1), whereas distractor coding predominated in V1 (error bars indicate 95% CI of between-subject variance; asterisks indicate significant pairwise model comparison). Relative to DLPFC, coding of incongruency predominated in dorsomedial frontal cortex (DMFC, including dACC and pre-SMA). At the individual level (right), subjects with stronger target coding in DLPFC, but weaker congruency coding in DMFC had smaller Stroop effects. C, In full factorial RSA, the precision of models can be boosted by adding specific manipulations to better isolate representations relevant to cognitive control.
