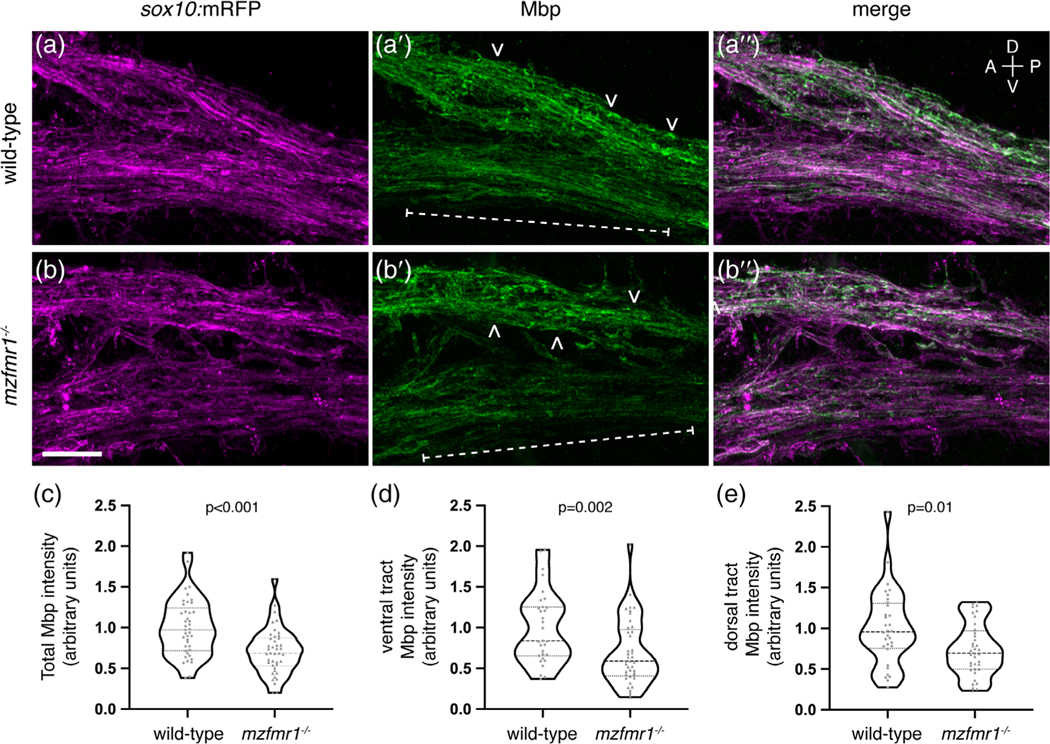
FIGURE 5.
Loss of fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) function leads to reduced Mbp protein expression. Sagittal sections through the hindbrain of Tg(sox10:mRFP) wild-type (a-a″) and mzfmr1−/− loss-of-function mutant (b-b″) larvae, labeled with antibody against Mbp. Mbp strongly co-localizes with sox10:mRFP+ myelin sheaths in the hindbrain. Mbp expression was quantified in both ventral (brackets) and dorsal myelin tracts (arrowheads). (c) Cumulative normalized quantification of Mbp intensity (wild-type n = 41 sections, 30 larvae; mzfmr1−/− n = 42 sections, 30 larvae; unpaired t test). (d) Normalized Mbp intensity in ventral hindbrain myelin tracts (wild-type n = 31 sections, 26 larvae; mzfmr1−/− n = 41 sections, 28 larvae; Mann–Whitney test). (e) Normalized Mbp intensity in dorsal hindbrain myelin tracts (wild-type n = 32 sections, 26 larvae; mzfmr1−/− n = 37 sections, 28 larvae; Mann–Whitney test). mRNA abundance in mzfmr1−/− mutants was normalized to wild-type. Scale bar = 10 μm. A = anterior, P = posterior, D = dorsal, V = ventral [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]