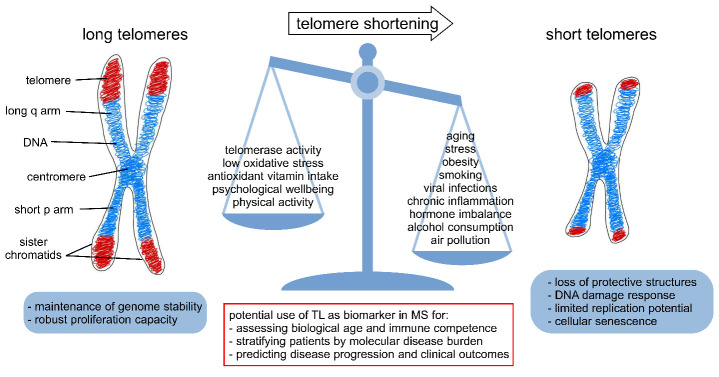
Figure 1.
Factors contributing to accelerated telomere shortening. A metaphase chromosome is depicted on the left. The telomeres are highlighted in red and not drawn to scale in the diagram. They are located at the ends of the chromosome arms and consist of TTAGGG tandem repeat sequences (5 - 15 kb in humans). The centromere holds the two sister chromatids together. In normal cells, telomeres shorten with every cell division. Apart from individual genetic determinants that affect telomere length (TL), various environmental and lifestyle factors are known to influence telomere attrition. Disruption of telomere maintenance is associated with end-to-end chromosome fusion. Critically short telomeres trigger DNA damage responses such as cell cycle arrest. Telomere biology thus plays a crucial role in health and disease. In multiple sclerosis (MS), the analysis of TL may serve as a biomarker of the patients’ immunosenescence status to assess and predict clinical disease phenotypes.