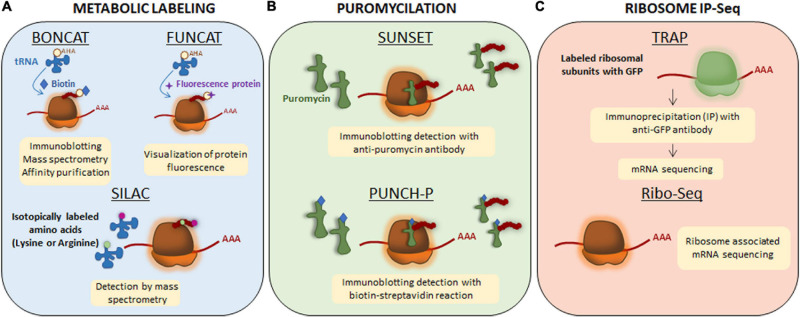
FIGURE 2.
Techniques to detect newly synthesized proteins. (A) Metabolic labeling. Bioorthogonal non-canonical amino acid tagging (BONCAT) and fluorescent non-canonical amino acid techniques (FUNCAT) are based on non-canonical methionine derivates (an azide or an alkaline) and therefore, they are able to get incorporated to the nascent protein as methionine through endogenous methyionil-transfer RNA (tRNA) synthetase. The newly synthesized proteins will be labeled with azide or alkyne groups. For their detection, exogenous reactive groups are then incorporated to azide or alkyne groups: biotin in BONCAT and a fluorescence protein in FUNCAT. For stable isotope labeling using amino acids in cell culture (SILAC), lysine and arginine are isotopically labeled with 12C (light amino acids) and 13C (heavy amino acids). The incorporation of labeled amino acids allows them to enter into newly synthesized proteins and be detected by mass spectrometry. (B) Puromycilation. Puromycin is an antibiotic that structurally mimics tRNAs so it can get incorporated into the nascent polypeptide chain and elongation is stopped. Puromycilated-proteins can be detected by immunochemistry directly using an anti-puromycin antibody for surface sensing of translation technique (SUNSET) or indirectly when puromycin is bound to biotin for puromycin-associated nascent chain proteomics (PUNCH-P). (C) Ribosome immunoprecipitation-sequencing (IP-Seq). Translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP) method consists on labeling ribosomal subunits with Green Fluorescence Protein (GFP) followed by immunoprecipitation approach. Transcripts bound to ribosomes containing GFP will be isolated and sequenced by RNA-sequencing. Ribo-Seq technique is based on sequencing all mRNA transcripts which are associated to ribosomes.