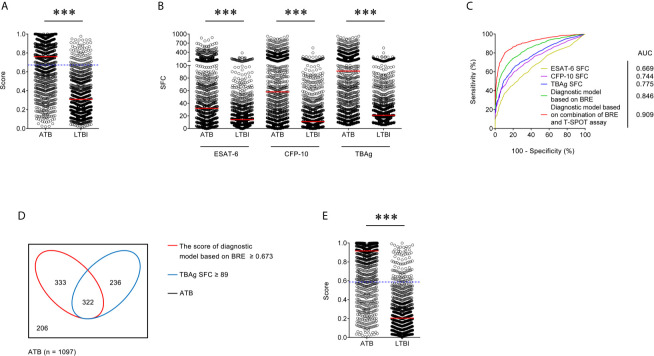
Figure 1.
Establishment of diagnostic model based on combination of BRE and T-SPOT in Qiaokou cohort. (A) Scatter plots showing the score of diagnostic model based on BRE in ATB patients (n = 1,097) and LTBI individuals (n = 962) in Qiaokou cohort. Horizontal lines indicate the median. ***P < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney U test). Blue dotted lines indicate the cutoff value in distinguishing these two groups. (B) Scatter plots showing ESAT-6 SFC, CFP-10 SFC, and TBAg SFC in ATB patients (n = 1,097) and LTBI individuals (n = 962) in Qiaokou cohort. Horizontal lines indicate the median. ***P < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney U test). (C) ROC analysis showing the performance of ESAT-6 SFC, CFP-10 SFC, TBAg SFC, diagnostic model based on BRE, diagnostic based on combination of BRE and T-SPOT in distinguishing ATB from LTBI in Qiaokou cohort. (D) Venn diagrams showing the overlap of the diagnostic model based on BRE and TBAg SFC in ATB patients (n = 1,097) in Qiaokou cohort. (E) Scatter plots showing the score of diagnostic model based on combination of BRE and T-SPOT in ATB patients (n = 1,097) and LTBI individuals (n = 962) in Qiaokou cohort. Horizontal lines indicate the median. ***P < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney U test). Blue dotted lines indicate the cutoff values in distinguishing these two groups. ATB, active tuberculosis; LTBI, latent tuberculosis infection; ESAT-6, early secreted antigenic target 6; CFP-10, culture filtrate protein 10; TBAg, tuberculosis-specific antigens; SFC, spot-forming cells; AUC, area under the curve; BRE, blood routine examination.