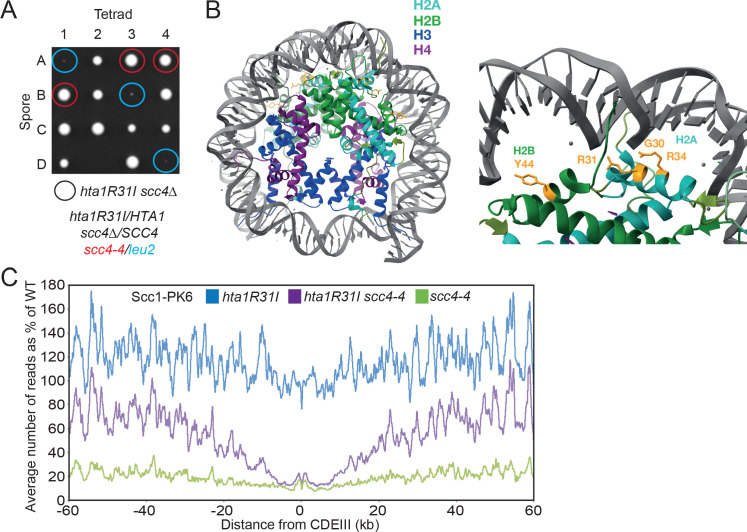
Figure 3. Mutations in SCC2 and histone genes also suppress scc4Δ lethality.
(A) Tetrad dissection of diploid strains containing SCC4/scc4Δ leu2/scc4-4 ΗTΑ1/hta1R31I. Spores in which scc4Δ is rescued by hta1R31I are circled in blue. (B) Structure of the yeast nucleosome (PDB: 1ID3; White et al., 2001). H2A is shown in blue and H2B in green. Suppressor mutations are shown in yellow. (C) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profiles of Scc1-PK6 in hta1R31I, scc4-4, and hta1R31I scc4-4 cells 60 kb either side of CDEIII plotted as a percentage of the average number of reads obtained for wild-type (W)T cells. Cells were pheromone arrested in G1 at 25°C before release at 35.5°C into medium containing nocodazole. Samples were taken 60 min after release (K22005, K24574, K24568, K22001).