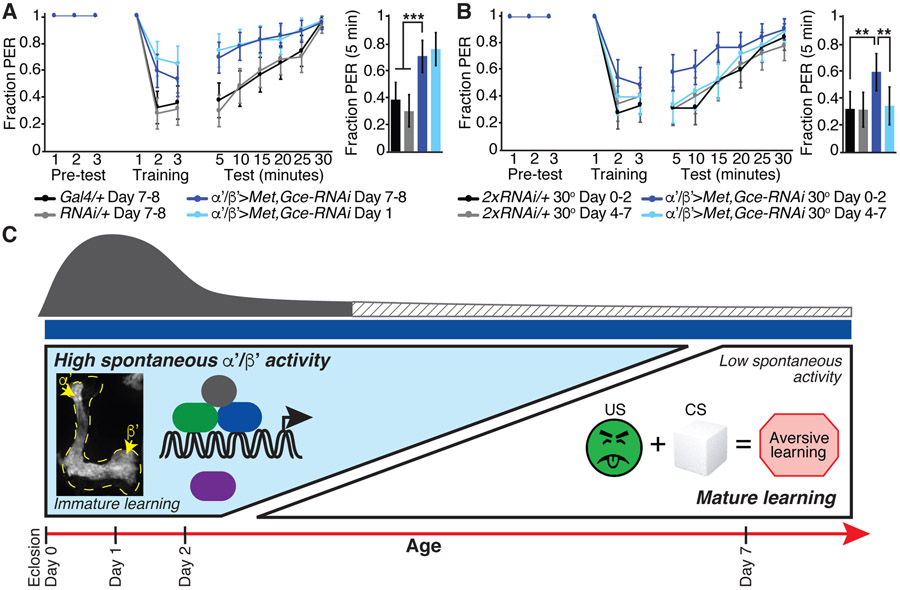
Figure 5. JH signaling in α’/β’ KCs is required during a young animal sensitive period for mature aversive taste memory behavior.
(A) Aversive taste memory of day 1 (light blue line) and day 7-8 flies (dark blue line) with Met and Gce knocked down in α’/β’ KCs and of the day 7-8 genetic controls (black and gray lines).
(B) Aversive taste memory of mature day 7-8 flies. Comparison of flies with Met and Gce knocked down in α’/β’ KCs only from day 0-2 (dark blue) or day 4-7 (light blue), when tub-GAL80ts repression is removed by shifting the flies to 30 degrees, and temperature-matched genetic controls.
(A and B) Bar graph represents data from the first 5 minute test period. N=47-62 flies, data shown as mean with 95% confidence interval error bars. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, Fisher’s Exact Test with Benjamini-Hochberg False Discovery Rate adjustment.
(C) Model for juvenile hormone (JH) signaling via Met and Gce receptors expressed in α’/β’ KCs from approximately eclosion to day 2 to drive a decrease in α’/β’ spontaneous neural activity and maturation of learned behavior, in particular aversive taste memory, by day 7 of adulthood. Representative standard deviation projection image shows high spontaneous activity in day 1 α’/β’ KCs. Spontaneous activity is mediated by Cacophony (Cac) voltage-gated calcium channels, and we hypothesize that Cac function may be indirectly downregulated with age by factors downstream of JH signaling which contribute to the excitability of α’/β’ KCs.