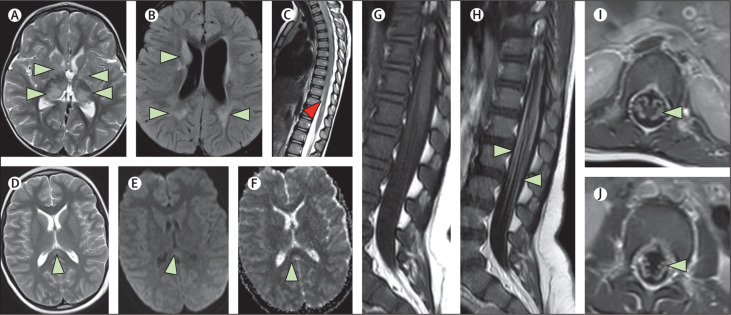
Figure 2.
MRI scans showing a range of neurological complications
(A, B, C) MRI brain and spine scans from a White girl aged 2 years with ADEM (case number 4, appendix p 7; the full patient history is given in appendix p 1). There are multiple hyperintense foci on the axial T2-weighted (A) and T2 FLAIR (B) images involving both cerebral hemispheres, including the basal ganglia, thalami, and subcortical and periventricular white matter (green arrows). Sagittal T2-weighted image of the spine (C) shows a focus of hyperintensity within the cord close to the conus (red arrow). (D, E, F) MRI brain scans from an Asian boy aged 11 years who presented with PIMS-TS, encephalopathy, and MERS (case number 48, appendix p 11; the full patient history is given in appendix p 1). Axial T2-weighted image (D) shows a focus of hyperintensity involving the splenium of the corpus callosum along the midline (green arrow). The B1000 (E) and the ADC maps (F) from the diffusion-weighted imaging shows subtle diffusion restriction involving the lesion. (G, H, I, J) MRI spine scans from an Asian boy aged 16 months who presented with Guillain-Barré syndrome (case number 8, appendix p 7; the full patient history is given in appendix p 2). Sagittal T1-weighted images before (G) and after contrast (H) show enhancement of the lumbosacral nerve roots (green arrows). The axial T1-weighted post-contrast images (I, J) show bilateral enhancement of the nerve roots. ADEM=acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. FLAIR=fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. PIMS-TS=paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19. MERS=mild encephalopathy with reversible splenial lesion. ADC=apparent diffusion coefficient.