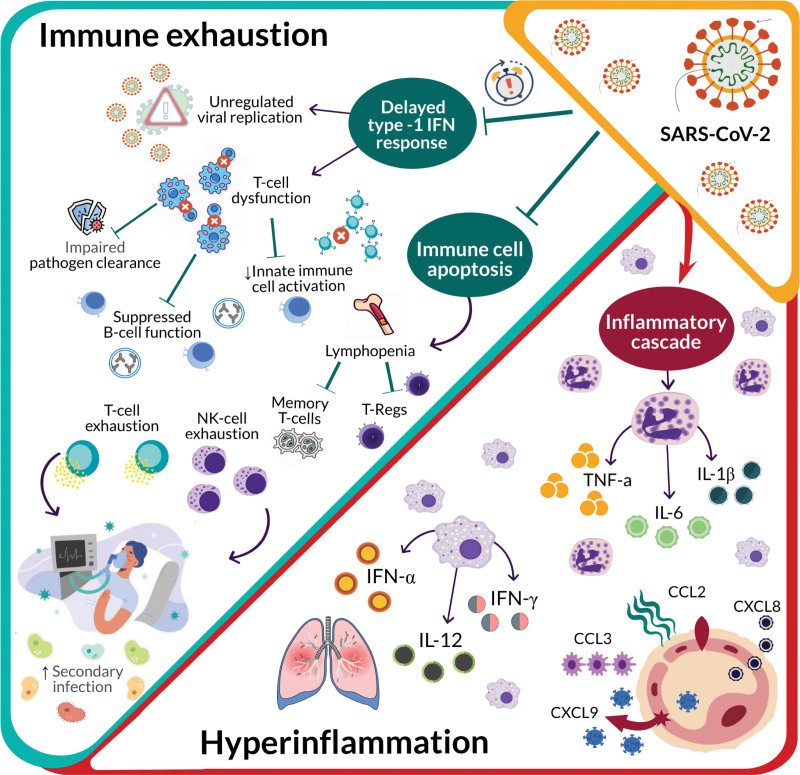
Figure 2.
Immunologic consequences of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)–associated immunosuppression. As infection persists, the host enters a state of immune exhaustion. A delayed or suppressed type-1 interferon (IFN) response leads to T-cell dysfunction and ultimately exhaustion. Furthermore, viral-induced immune cell apoptosis results in lymphopenia with decreases in all lymphocyte subtypes. Continued activation of the inflammatory cascade leads to increasing levels of inflammatory cytokines and hyperinflammation. Hyperinflammation paired with immune exhaustion places patients at an increased risk of secondary infectious complications. CCL = C–C motif chemokine ligand, CXCL = C-X-C motif chemokine ligand, IL = interleukin, NK = natural killer, TNF-a = tumor necrosis factor alpha.