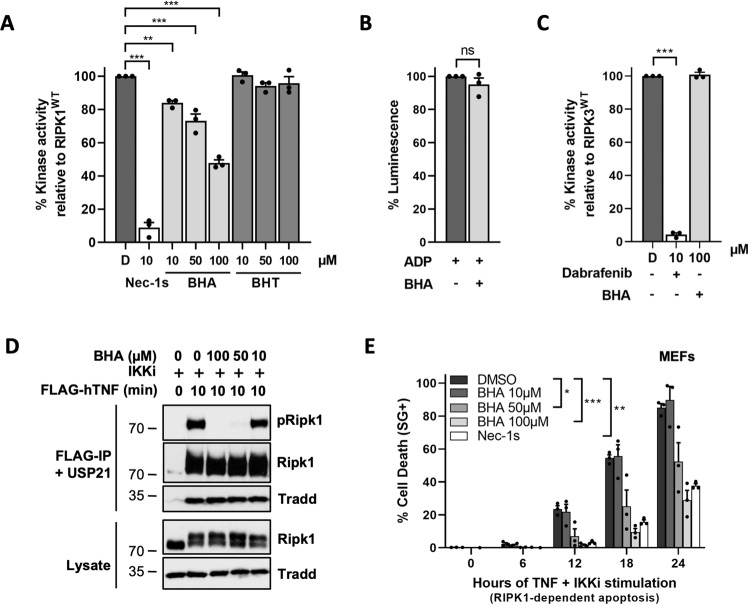
Fig. 4. BHA acts as a direct RIPK1 kinase inhibitor.
A, C Quantitative RIPK1 (AA 1–479) (A) or Ripk3 (AA 1–439) (C) enzymatic activities were measured by ATP consumption using ADP-Glo kinase assays. The compounds were used at indicated concentrations and ‘D’ is short for DMSO. B The ADP-Glo reaction was performed in the absence of active kinase to assess the possible interference of BHA (100 µM) with the luminescence reaction. Results are presented as a percentage relative to the activity of the RIPK1/3 in absence of inhibitors (A, C), or as a percentage relative to the ADP-Glo luminescence reaction (B) and are the mean ± SEM of three independent kinase assays (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey post hoc test (A–B) or by a two-tailed paired t test (C). D MEFs were pretreated for 30 min with the indicated compounds (5 µM TPCA-1) before stimulation with 1 µg/ml FLAG-hTNF for the indicated duration. TNFR1 complex I was then FLAG-immunoprecipitated and the IPs were treated with USP21 before analysis by immunoblot, where pRIPK1 refers to autophosphorylation of RIPK1 on S166/T169. The results are representative of at least two independent experiments. E MEFs were pretreated for 30 min with the indicated compounds before stimulation with 20 ng/ml hTNF for the indicated duration. Cell death was measured over time by Sytox Green (SG+) positivity, and the results are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical analysis on kinetic cell death assays with more than one timepoint is detailed in the Methods section (E). Significance between samples is indicated in the figures as follows: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant.