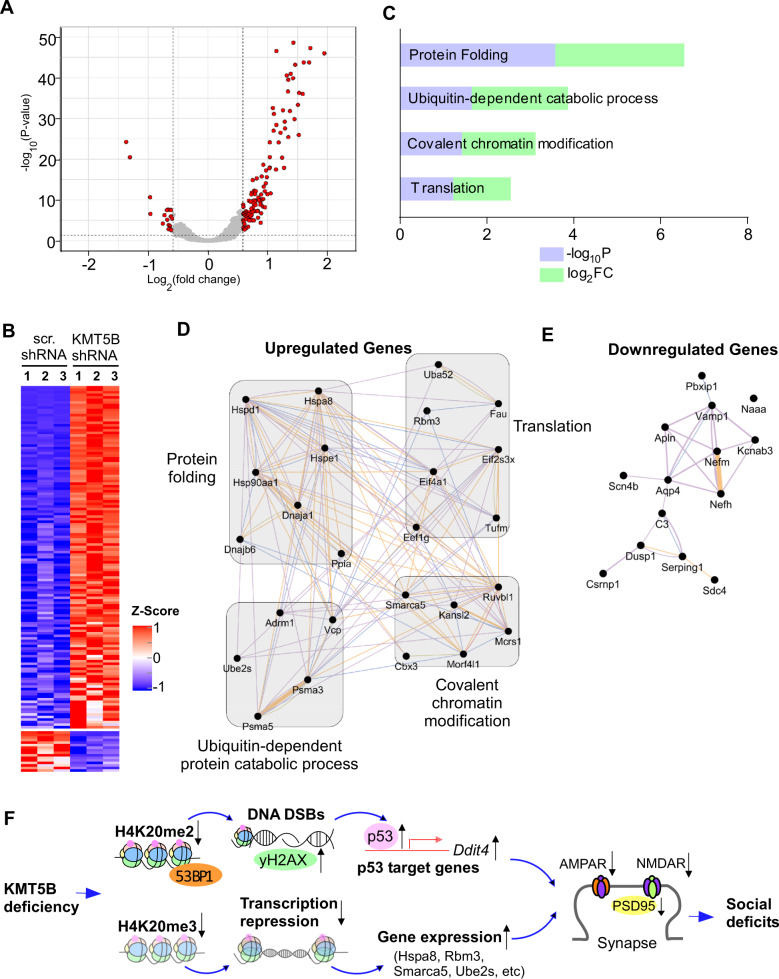
Fig. 5. Transcriptomic changes in Kmt5b-deficient PFC.
A Volcano plot showing the transcriptomic distribution in PFC from mice injected with Kmt5b shRNA or scr. shRNA AAV. Significant DEGs are indicated in red circles. B Heat maps representing expression (row z-score) of genes that were significantly up- or downregulated in PFC from mice injected with Kmt5b shRNA or scr. shRNA AAV (n = 3 each group). C Enriched pathways identified via gene ontology analysis of upregulated DEGs in Kmt5b-deficient PFC. Interactome network of upregulated (D) or downregulated (E) genes. Purple lines indicate co-expression; blue lines indicate co-localization. F A schematic model showing the potential mechanism underlying the effects of Kmt5b deficiency in PFC. Kmt5b deficiency-induced loss of H4K20me2 impairs 53BP1-mediated DNA repair, leading to the activation of p53 and its target gene Ddit4 (Redd1). On the other hand, Kmt5b deficiency-induced loss of H4K20me3 reduces transcriptional repression, leading to the upregulation of genes enriched in cellular stress response and ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation. Collectively, it leads to the diminished PFC glutamatergic synaptic transmission and synaptic protein expression. Consequently, mice with Kmt5b deficiency in PFC display social deficits, a core symptom of autism.