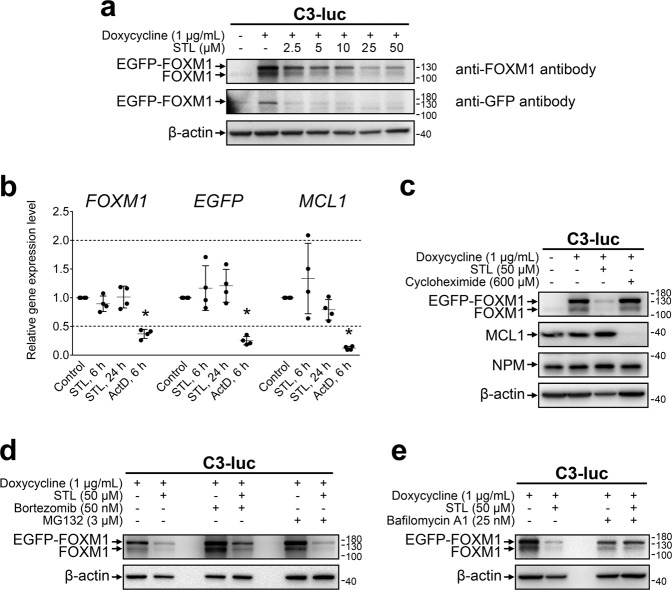
Fig. 2. STL inhibits FOXM1 expression on protein level via autophagy-dependent mechanism.
a C3-luc cells stimulated with doxycycline to induce expression of EGFP-FOXM1 fusion protein were treated with increasing concentrations of STL for 24 h. Total protein samples were analyzed via immunoblotting for FOXM1 and GFP expression, β-actin was used as an internal loading control. b Doxycycline-stimulated C3-luc cells were treated with 50 μM STL for 6 or 24 h and 10 μg/mL ActD for 6 h. Total RNA samples were analyzed for FOXM1, GFP, and MCL1 transcript levels via RT-qPCR, 18 S rRNA was used as a reference transcript. Data are presented as means ± S.D. and individual datapoints, N = 4, * – exact p = 0.02857 (Mann–Whitney U test, two-tailed). c C3-luc cells were treated with indicated concentrations of doxycycline, STL, or CHX for 24 h. Total protein samples were analyzed via immunoblotting for FOXM1, NPM, and MCL1 expression, β-actin was used as an internal loading control. d Doxycycline-stimulated C3-luc cells were treated with STL for 24 h in the presence of bortezomib or MG132. Total protein samples were analyzed via immunoblotting for FOXM1 expression, β-actin was used as an internal loading control. e Doxycycline-stimulated C3-luc cells were treated with STL for 24 h in the presence of bafilomycin A1. Total protein samples were analyzed via immunoblotting for FOXM1 expression, β-actin was used as an internal loading control.