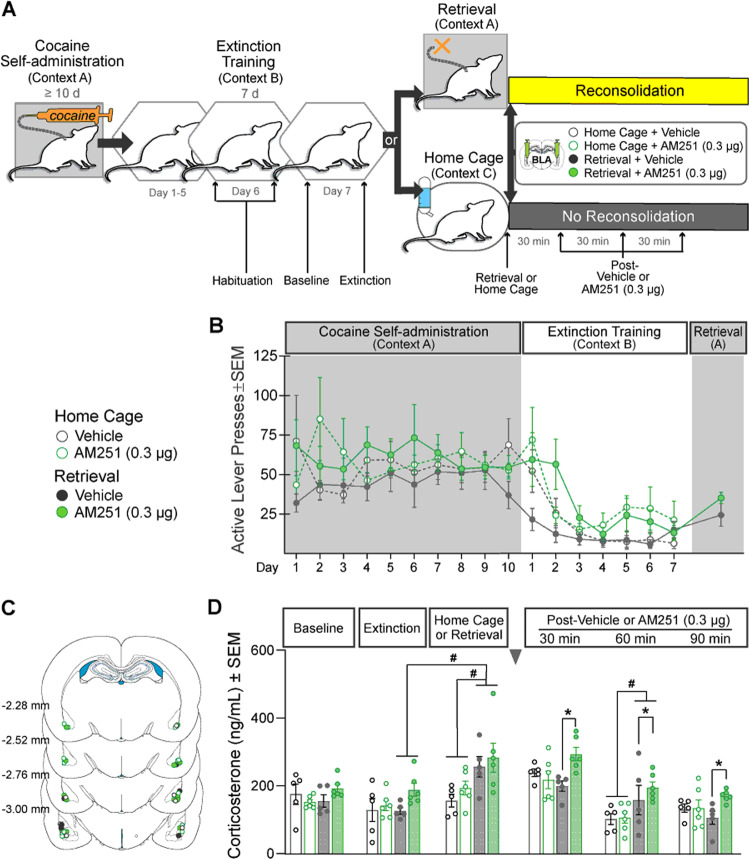
Fig. 5. Intra-BLA AM251 administration prolongs memory retrieval-induced increase in blood serum corticosterone concentrations during cocaine-memory reconsolidation.
A Experimental timeline. Rats received cocaine self-administration training in one context (cocaine-paired context, Context A) and extinction training in a different context (extinction context, Context B). Rats were habituated to the tail-nick procedure before and after extinction session 6 (Habituation). Blood samples were collected immediately prior to extinction session 7 (Baseline), after extinction session 7 (Extinction), after either the 15-min cocaine memory-retrieval session (Retrieval) or comparable exposure to the home cage (Home Cage), and after intra-BLA infusions of AM251 (0.3 µg/0.5 µL per hemisphere) or vehicle at 30-min intervals (30, 60, 90; n = 5–6/group). B Active-lever responses (mean ± SEM) during cocaine self-administration (last 10 days), extinction training, and during the 15-min cocaine-memory retrieval session prior to treatment manipulations. C Schematic of cannula placements in the BLA with symbols representing the most ventral point of injection cannula tracts for rats that were re-exposed to the cocaine-paired context or home cage followed by vehicle or AM251 treatment. D Blood serum corticosterone concentrations (mean ± SEM) at baseline, immediately after exposure to the extinction context, the home cage, or the cocaine-paired context (i.e., cocaine-memory retrieval), and at 30, 60, and 90 min post treatment. Symbols: #context simple-main effect, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s tests, ps < 0.05 or #retrieval simple-main effect, 2 × 2 × 3 ANOVA, retrieval x time, Sidak’s test, p < 0.05; *treatment simple-main effect, 2 × 2 × 3 ANOVA, retrieval × treatment, Sidak’s test, p < 0.05.