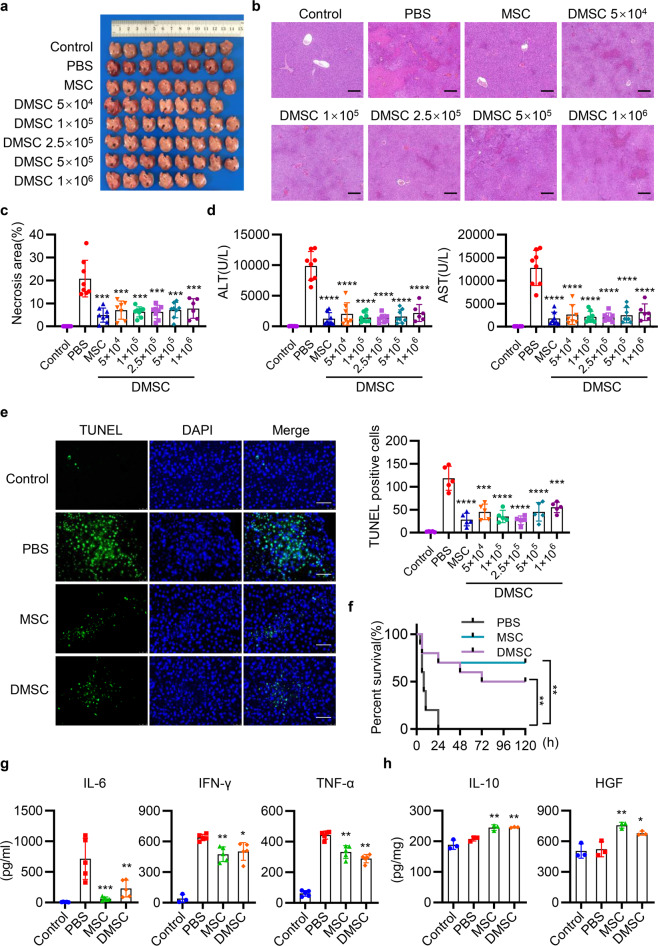
Fig. 2.
MSCs and DMSCs attenuate ConA-induced liver injury in mice. a Mice were intravenously injected with 12 mg/kg ConA, followed by intravenous injection with PBS, 1 × 106 MSCs (containing 5 × 104 DMSCs) or 5 × 104 to 5 × 106 DMSCs. Twelve hours after administration of ConA, mice were killed and representative macroscopic images of livers were shown. n = 6~8. b Representative images of liver histopathology with H&E staining. Scale bar represents 200 μm. c–e Quantitative analysis of necrotic area (c), serum ALT and AST levels (d), and TUNEL-positive cells (e, scale bar represents 50 μm) in mice with PBS, MSCs, or DMSCs treatment after ConA injection. n = 6~8 in c, d and n = 5 in e. f Survival of 25 mg/kg ConA-injected mice treated with PBS, MSCs, and DMSCs. n = 10. g, h The levels of IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in serum (g), and IL-10 and HGF in hepatic tissues (h) were determined by ELISA in each group. n = 3~5 in each group. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was performed. Statistical significance is indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, compared with PBS group