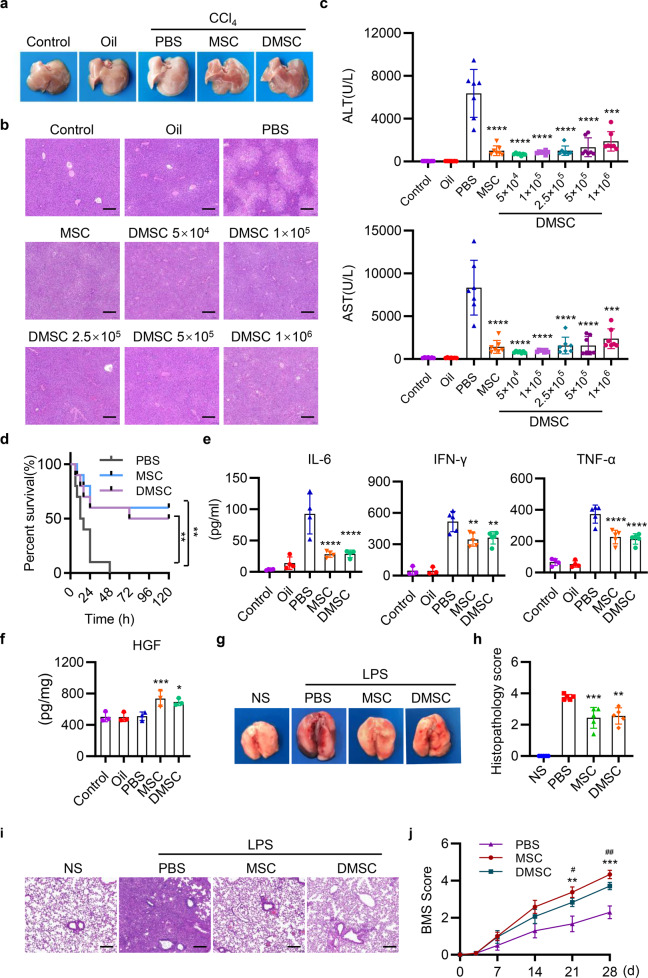
Fig. 3.
MSCs and DMSCs attenuate tissue injury in mice. a Mice were intraperitoneally injected with 0.5 ml/kg CCl4, followed by intravenous injection with PBS, MSCs, or DMSCs. Representative macroscopic images of livers 24 h after CCl4 injection. b Representative images of liver histopathology with H&E staining 24 h after CCl4 administration. Scale bar represents 200 μm. c Quantification of serum AST and ALT after CCl4 injection in each group. n = 7 in each group. d Survival 5 ml/kg CCl4-injected mice treated with PBS, MSCs, and DMSCs. n = 10. e, f The levels of IL-6, IFN-γ, TNF-α in serum (e) and HGF in hepatic tissues (f) were determined by ELISA in each group. n = 3~5 in each group. g Mice were intratracheally instilled with 5 mg/kg LPS, followed by intravenous injection with PBS, MSCs, or DMSCs. The representative macroscopic images of the lungs 72 h after LPS administration were shown. h, i Representative images of lung histopathology with H&E staining (i) and histopathology score (h) 72 h after LPS administration. Scale bar represents 200 μm. j MSCs and DMSCs improved the behavior of mice in spinal cord injury model. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, compared with PBS group in c–f, h. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, MSC compared with PBS group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, DMSC compared with PBS group in j