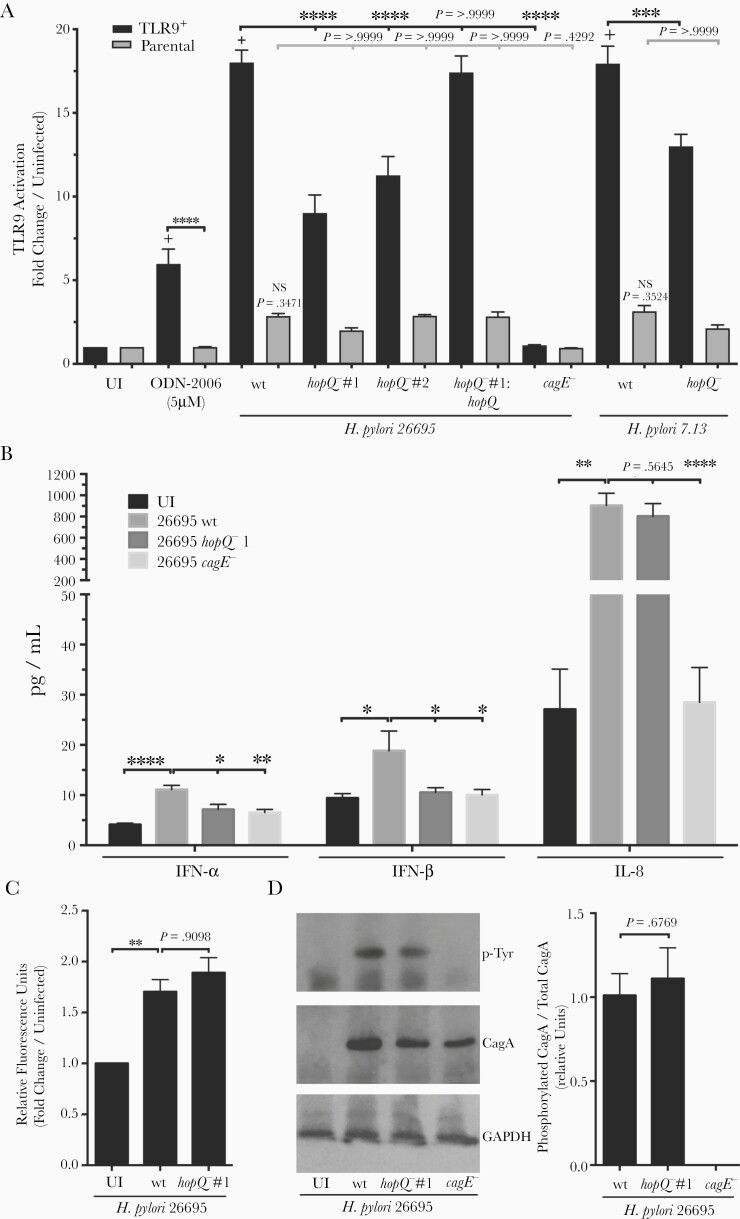
Figure 2.
Deletion of hopQ significantly decreases TLR9 activation independent of cellular adhesion and cag-T4SS function. A, TLR9-reporter or parental cells were challenged with TLR9 agonist ODN-2006, Helicobacter pylori wild-type cag-PAI+ strain 26695, wild-type cag-PAI+ strain 7.13, respective hopQ− or cagE− isogenic mutant strains, or a complemented 26695 hopQ mutant. Samples were tested in duplicate at least 3 times and data are fold change in infected over uninfected controls. B, Levels of IFN-α, IFN-β, and IL-8 were determined via ELISA in H. pylori:AGS cell supernatants. In each experiment, strains were tested at least 3 times and mean ± SEM are shown. C, Fluorescently labeled H. pylori wild-type strain 26695 or a 26695 hopQ− isogenic mutant were co-cultured with AGS cells for 4 hours and analyzed for fluorescence. Strains were tested in duplicate and data are fold change of infected over uninfected control. D, CagA translocation was determined by quantifying levels of phospho-CagA in AGS cell lysates during H. pylori co-culture by Western blotting. Representative Western blots and densitometric analysis normalizing levels of phosphorylated CagA to total CagA from 3 replicates are shown. GAPDH served as a loading control. ANOVA with Bonferroni correction or student t test was used to determine statistical significance between groups. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001; + P < .00001 compared to uninfected TLR9+ cells; NS, nonsignificant compared to uninfected parental cells. Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IFN, interferon; IL-8, interleukin-8; TLR9, Toll-like receptor 9; UI, uninfected; wt, wild type.