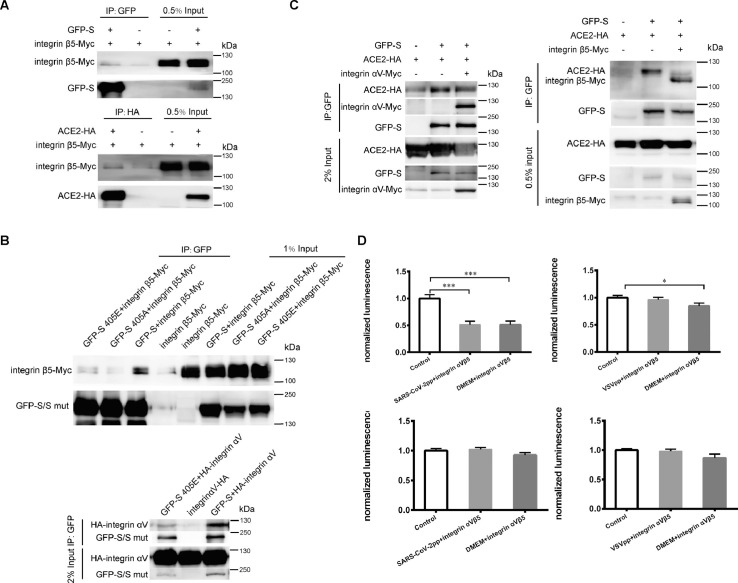
Fig. 1.
Integrin inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection through inhibition of S-ACE2 binding. (A) Integrin β5 interacted with SARS-CoV-2 S and ACE2. Top, Myc-tagged integrin β5 with or without GFP-tagged S was transfected into 293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-GFP antibody. Bottom, integrin β5-Myc was expressed in 293T cells with or without ACE2-HA. Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-HA antibody. (B) RGD motif in S protein was important for its binding with integrin β5 and integrin αV. Top, Wild type S and two single-amino acid mutants (405E, 405A) were expressed in 293T cells receptively with integrin β5-Myc. Bottom, wild type S or S 405E mutant was expressed in 293T cells. Lysates was immunoprecipitated by GFP. (C) SARS-CoV-2 S and ACE2 interaction was inhibited by integrin αV and integrin β5. Left, GFP-tagged full-length S and HA-tagged ACE2 were co-expressed in 293T cells with or without Myc-tagged integrin αV. Right, GFP-S and ACE2-HA were transfected with or without integrin β5-Myc. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by GFP antibody. (D) Integrin αVβ5 protein inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection. 293T cells were transiently transfected with ACE2-expressing plasmid. Left top: SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus and ACE2-expressing cells were separately treated with recombinant human integrin αVβ5 protein. Then the 293T cells were infected by SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus for 48 h and pseudovirus entry was indicated with luciferase activity. Left down: Cell viabilities were measured. Right top: ACE2-expressing 293T cells and VSVpp were pretreated with integrin αVβ5 protein. Then the cells were infected with integrin αVβ5 conditioned or unconditioned VSVpp. Luciferase activity was measured after 48 h. Right down: Cell viability under two conditions were not affected.