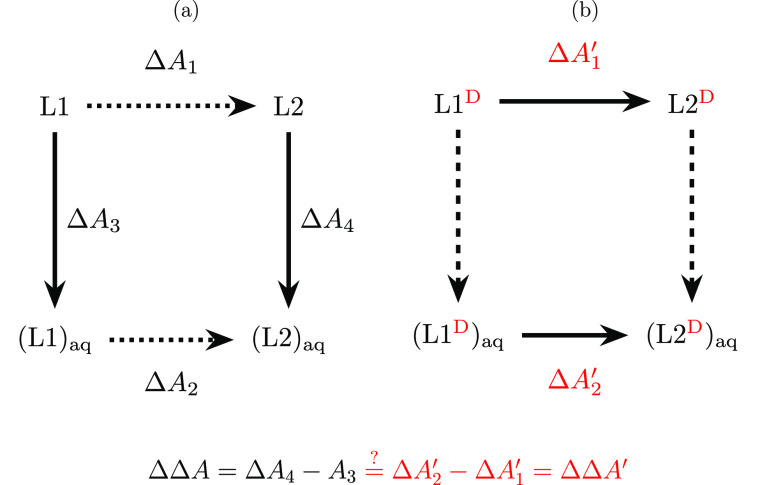
Figure 1.
(a) Idealized thermodynamic cycle used to compute the relative solvation free energy difference between two solutes, L1 and L2. Since the free energy is a state function, ΔΔA = ΔA4 – ΔA3 = ΔA2 – ΔA1.7 The horizontal, dashed arrows indicate the idealized alchemical paths in the absence of dummy atoms. (b) Thermodynamic cycle required in practice whenever the number of atoms in L1 and L2 is not the same. The presence of dummy atoms is indicated by the superscript D. For example, L1D denotes ligand L1 including any dummy atoms attached to make the number of atoms at the two end states identical. Thus, along the horizontal, alchemical paths one computes ΔΔA′ = A2′ – A1, rather than ΔΔA = A2 – A1.