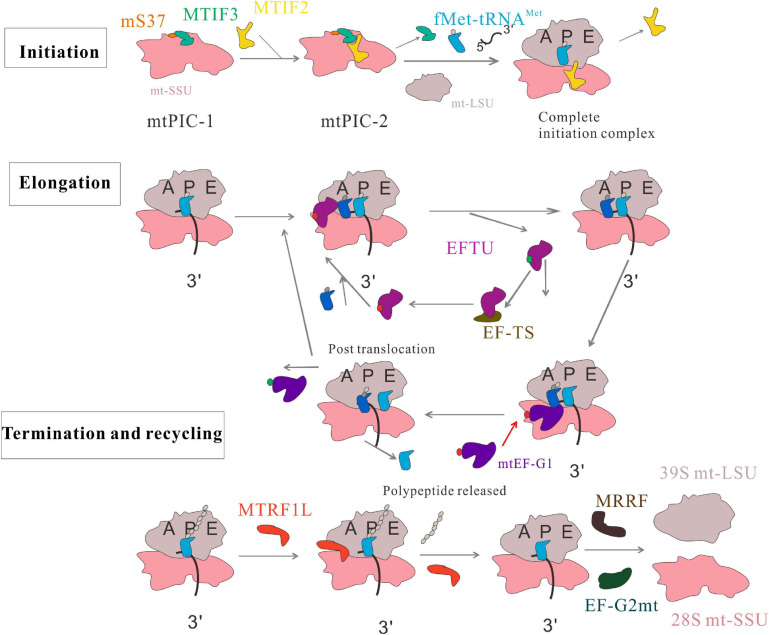
FIGURE 1.
Human mitochondrial translation. The process includes four phases: initiation, elongation, termination, and recycling. In the initiation phase, two distinct pre-initiation assembly steps, termed mitochondrial preinitiation steps 1 and 2 (mtPIC-1, mtPIC-2) are established. In the elongation phase, the aminoacyl-tRNA is transferred to the A site of mitochondrial ribosome by GTP ⋅ EFTU, and GTP ⋅ EFTU is transformed into GDP ⋅ EFTU. EF-TS converts GDP ⋅ EFTU to GTP ⋅ EFTU. The peptide-tRNA in the P site is transferred from the P site to the A site. mtEF-G1 binds to the ribosome at the A site and promotes translocation of the ribosome along the mRNA by inducing movement of A-tRNAs and P-tRNAs to the P site and E site. The tRNA at the E site leaves the monomer and this cycle continues until the polypeptide is completed and the stop codon appears at the A site. MRRF and EF-G2mt promote the separation of ribosomal subunits; MTIF3 combines with the small mitochondrial ribosomal subunits to prevent the premature reassociation of the large and small subunits.