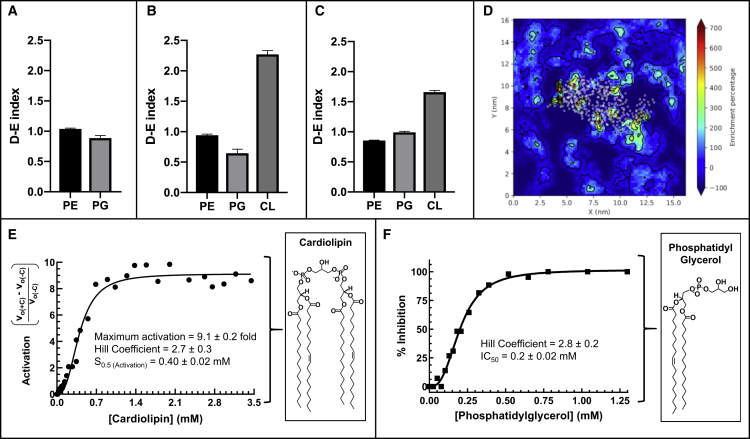
Figure 6.
Interactions between MurM and membrane phospholipids
(A–C) Depletion-enrichment (D–E) indices for phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and cardiolipin (CL) occurring within a 1.1-nm perimeter of the MurM protein for (A) Systems 4 and 5 (molar ratio of 75% phosphatidylethanolamine and 25% phosphatidylglycerol), (B) Systems 6 and 7 (molar ratio of 76% phosphatidylethanolamine, 16% phosphatidylglycerol, and 8% cardiolipin), and (C) Systems 8 and 9 (molar ratio of 72% phosphatidylethanolamine, 12% phosphatidylglycerol, and 16% cardiolipin). The D-E index was determined from 150 to 250 ns in 50-ns blocks for all repeats for a total of eight values per plot.
(D) Example of a D-E map with MurM at the membrane. White dots represent the center of geometry of each protein amino acid residue, and the percentage enrichment of phospholipid is indicated by the color.
(E) Activation of MurM was calculated as the product of subtraction of MurM velocity in the absence of cardiolipin (v0(−C)) from MurM velocity in the presence of cardiolipin (v0(+C)) divided by v0(−C) and was plotted versus cardiolipin concentration.
(F) Inhibition of MurM was calculated as [(v0(-PhG)) − (v0(+PhG))]/v0(−PhG) × 100 (where PhG denotes phosphatidylglycerol) and was plotted versus phosphatidylglycerol concentration. Data were fitted as described in the text. GraphPad Prism (version 8.4.1) and Matplotlib (version 3.0.3) were used for data analysis and figure preparation.
See also Figure S2.