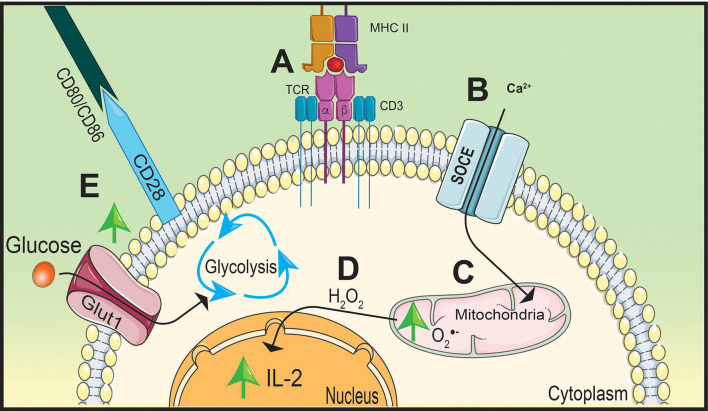
Figure 2.
Stimulation of TCR and CD28 causes a metabolic shift in naïve CD4 T cells. T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation by peptide presented on major histocompatibility complex-II (MHC-II) (A) will increase calcium (Ca2+) entry into the cytoplasm through store operated calcium entry (SOCE) channels (B) increasing mitochondrial-derived superoxide generation (C). Oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) will promote interleukin (IL)-2 expression by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) signaling (D). Simultaneously, CD28 will upregulate Glut1 expression on the cell membrane increasing glucose uptake shifting metabolism away from OxPhos to glycolysis to support rapid proliferation (E).