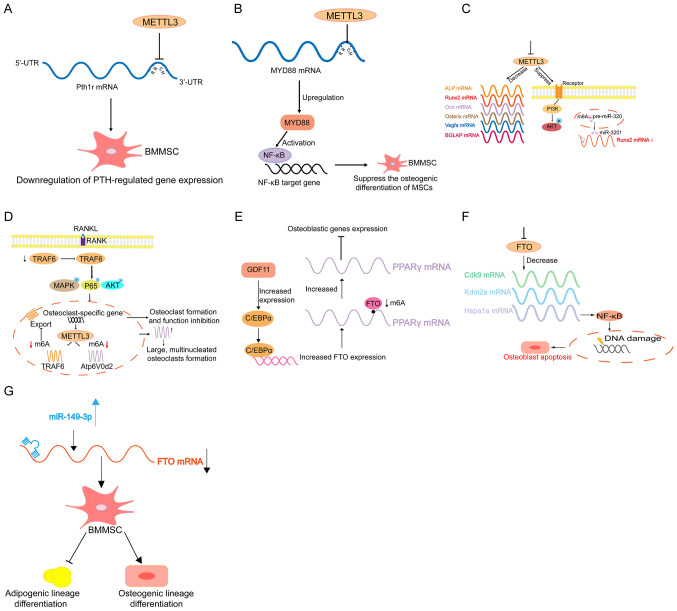
Figure 3.
Schematic model of m6A in regulating osteoporosis. (A) METTL3 knockout decreases the translation efficiency of BM. BMMSCs lineage allocator Pth1r and disrupts PTH-induced osteogenic and adipogenic responses. (B) METTL3 positively regulates the expression of MYD88 by facilitating the modification of m6A methylation to MYD88-RNA and subsequently induces the activation of NF-κB to suppress osteogenic progression. (C) METTL3 deficiency results in decreased expression levels of RUNX2, Osterix, Ocn, VEGFA, BGLAP, and ALP, and suppresses the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway. METTL3 silencing also decreases RUNX2 mRNA levels through the suppression of the m6A of precursor (pre-)miR-320, which targets RUNX2. (D) METTL3 knockdown causes the retention of TRAF6 mRNA in the nucleus, which results in the inactivation of RANKL-induced signalling pathways, suppression of osteoclast-specific gene expression and inhibition of osteoclast formation and function. METTL3 knockdown upregulates Atp6v0d2 mRNA expression and stability and leads to the formation of large, multinucleated osteoclasts. (E) GDF11 upregulates C/EBPα to promote the expression of FTO during osteoporosis. Increased FTO levels results in the demethylation of Pparg mRNA and leads to an increase in Pparg mRNA levels, which affect the differentiation of BMMSCs (10). Disruption of FTO leads to changes in the transcripts of Hspa1a and other genes in the DNA repair pathway in osteoblasts. (F) FTO-deficiency-mediated downregulation of Hspa1a in osteoblasts activates the NF-κB signalling pathway and results in the increased susceptibility of osteoblasts genotoxic agents and increased rates of apoptosis. (G) miR-149-3p represses the expression of FTO genes by binding to the 3'-UTR of the FTO mRNA to decrease the adipogenic differentiation potential of BMMSCs and increase osteogenic differentiation potential. m6A, RNA N6-methyladenine; METTL, methyltransferase-like; BMMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; NF, nuclear factor; Runx2, runt-related transcription factor 2; VEGF, vascular endothelial factor; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; miR, microRNA; FTO, fat-mass and obesity-associated protein; UTR, untranslated region.