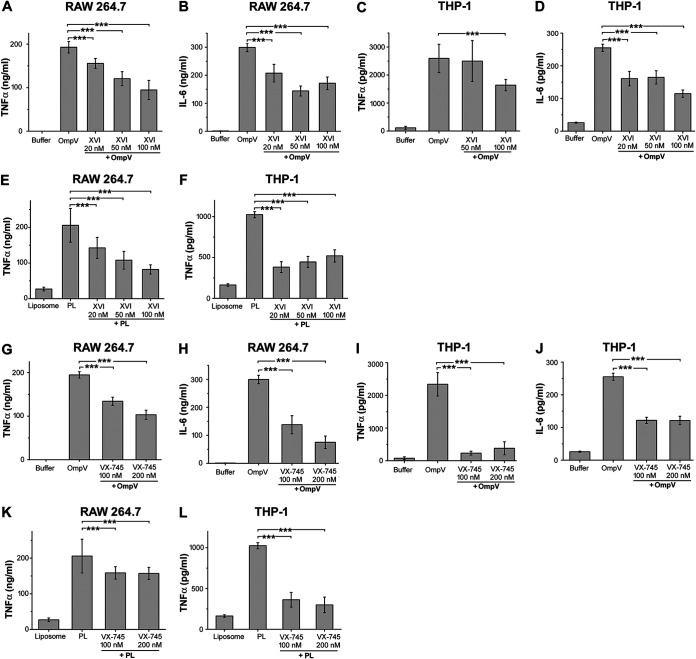
FIG 9.
p38 and JNK are involved OmpV-mediated signaling. (A to D) A significant decrease in TNF-α and IL-6 production was observed upon pretreatment with JNK inhibitor in OmpV-activated macrophages (A, B) and monocytes (C, D). (E, F) JNK is involved in OmpV-proteoliposome (PL)-mediated proinflammatory signaling. (A to F) RAW 264.7 macrophages (A, B, E) and THP-1 monocytes (C, D, F) were pretreated with JNK inhibitor followed by treatment with PmB and OmpV (A to D) or OmpV-proteoliposome (PL) (E, F). Following incubations, supernatants were analyzed for proinflammatory cytokines by ELISA. Bar graphs are expressed as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, P > 0.05 versus only OmpV-treated cells (A to D) or OmpV-proteoliposome (PL)-treated cells (E, F). (G to J) A significant decrease in TNF-α and IL-6 was observed upon pretreatment with p38 inhibitor in OmpV-activated macrophages (G, H) and monocytes (I, J). (K, L) p38 is involved in OmpV-proteoliposome (PL)-mediated signaling in macrophages and monocytes. RAW 264.7 (G, H, K) and THP-1 cells (I, J, L) were pretreated with p38 inhibitor followed by treatment with PmB and OmpV or OmpV-proteoliposome (PL). Following incubations, supernatants were collected and analyzed for proinflammatory cytokines by ELISA. Bar graphs are expressed as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, P > 0.05 versus only OmpV-treated cells (G to J) or OmpV-proteoliposome (PL)-treated cells (K, L).