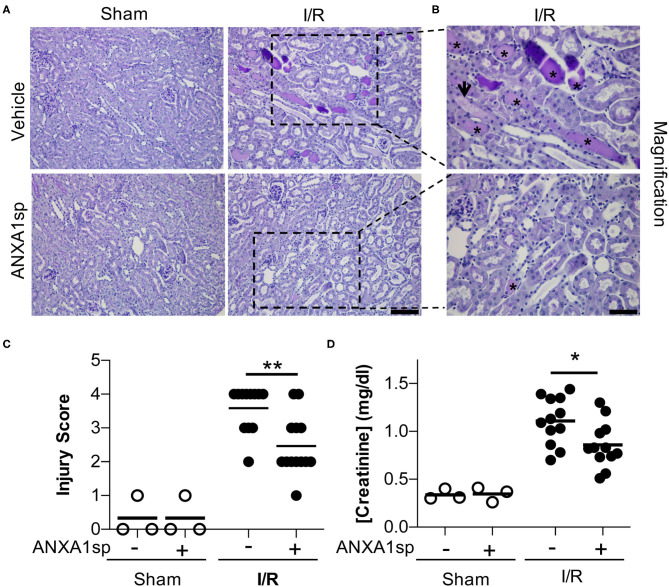
Figure 1.
AnnexinA1 tripeptide (ANXA1sp) attenuates kidney injury following ischemia/reperfusion-induced kidney injury. Mice were treated with either Vehicle or ANXA1sp and subjected to 33 min of unilateral ischemia and contralateral nephrectomy and then re-injected with Vehicle or ANXA1sp 1 h after reperfusion. (A) Representative periodic-acid Schiff (PAS)-stained kidney sections demonstrating increased injury in Vehicle, I/R group at Day 1 after ischemia (scale bar = 100 um). (B) Increased magnification of boxes in (A) to demonstrate increased histologic evidence of injury in Vehicle, I/R mice (asterisk: protein casts; arrowhead: tubule vacuolization) compared to ANXA1sp-treated mice (scale bar = 50 um). (C) Histologic injury scoring from (A) by observer blinded to experimental grouping (n = 3 for Sham groups, n = 12 for I/R groups). ANXA1sp-treated mice display attenuated kidney injury. Statistical significance determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak post-test (**p < 0.01). (D) Serum creatinine was measured. ANXA1sp-treated mice display ameliorated AKI compared to Vehicle-treated mice (n = 3 for Sham groups, n = 12 for I/R groups). Line on graph displays mean. Statistical significance determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak post-test (*p < 0.05).