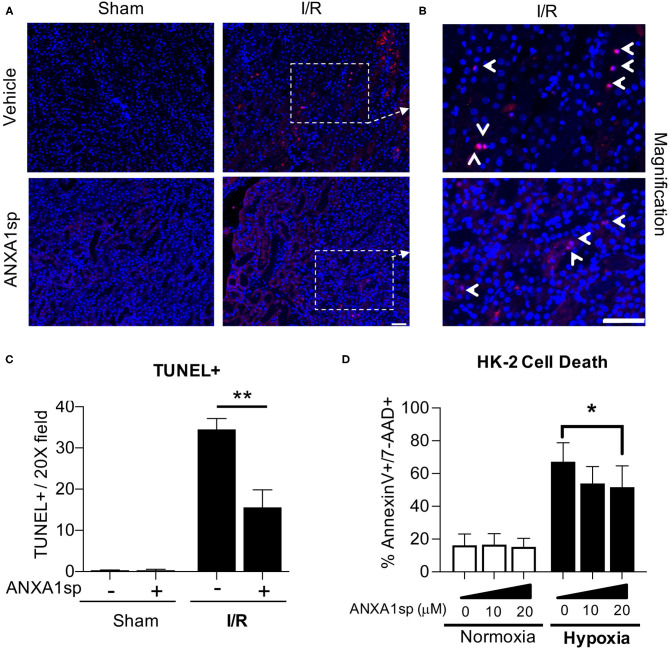
Figure 2.
ANXA1sp treatment prevents kidney tubular cell death. Mice were treated with either Vehicle or ANXA1sp 1 h prior to ischemia, subjected to 33 minutes of unilateral ischemia and contralateral nephrectomy and then re-injected with Vehicle or ANXA1sp 1 h after reperfusion. (A) Kidney tissues were harvested at 24 h after reperfusion. Representative terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-stained kidney sections demonstrating increased apoptosis in Vehicle, I/R group at Day 1 after ischemia. Scale bar shows 25 μm. (B) Increased magnification of boxes in (A) to demonstrate increased evidence of apoptosis in Vehicle, I/R mice (arrowhead: TUNEL-positive nuclei) compared to ANXA1sp-treated mice. Scale bar shows 25 μm. (C) Quantification of TUNEL positive nuclei from (A). Graph displays mean +/- SEM of % TUNEL positive nuclei from five fields/section from each mouse (n = 3 for Sham and I/R groups) with significance determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak post-test (**p < 0.01). (D) The immortalized human kidney cell line, HK-2, was grown to confluence in monolayers. Cells were pretreated with Vehicle or ANXA1sp at increasing concentrations and then subjected to 16 h of oxygen-glucose deprivation (hypoxia) in an anaerobic chamber. ANXA1sp prevented hypoxic cell death (n = 5–6/condition). Graphs display mean +/- SEM with significance determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak post-test (*p < 0.05).