Fig. 2 |. Control of the UCST cloud point using main-chain amino acid composition.
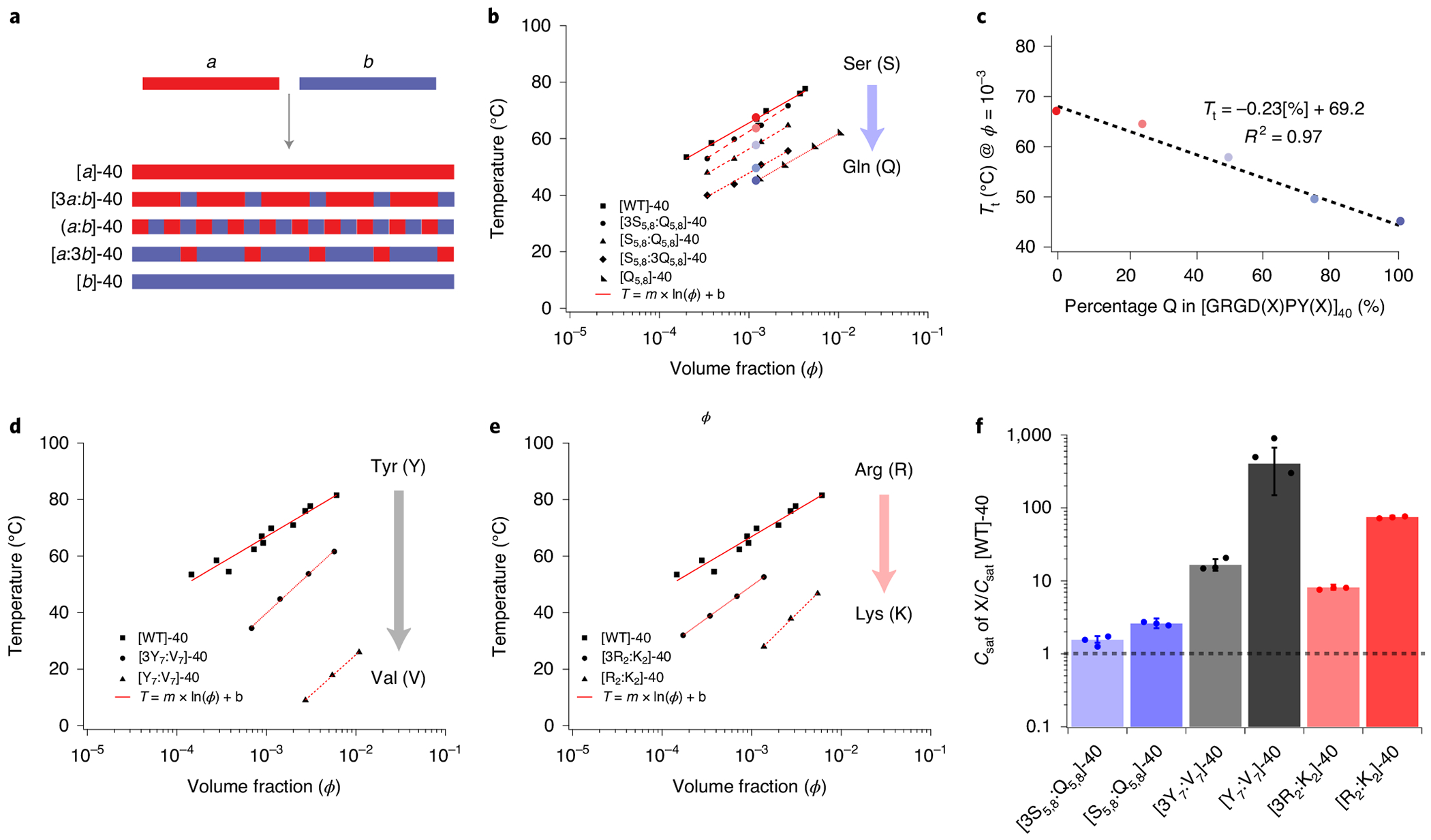
a, A schematic describing the methodology for doping repeat unit b into a homopolymer of a. The WT A-IDP, with a high UCST cloud point comprising 40 repeats of a (GRGDSPYS), is doped with increasing fractions of repeat b (GRGDQPYQ) to probe the loss of function of UCST phase behaviour from polymers of a. The doping of b into a is designed to ensure mixing of the two repeats along the polypeptide chain and minimize blocky behaviour. b, Doping of b into a results in mutant IDPs; the UCST Tt of each mutant IDP is a linear function of the ϕ of the A-IDP. c, The effect of composition (degree of doping) is a linear function of the degree of substitution of b into a at a constant ϕ of 10−3 (25–30 μM) (R2 = 0.97). d, Substitution of aromatic Y residues by aliphatic V dramatically reduces Tt. e, Substitution of R by K dramatically reduces Tt; 50% substitution lowers the Tt by more than 40 °C. f, The chemical composition can affect the saturation concentration by two orders of magnitude at constant molecular weight (Csat @ 37°C = 1–800 μM). This can be visualized by normalizing to the saturation concentration of [WT]-40, which is conveniently ~1 μM and is shown by the dashed horizontal line.
