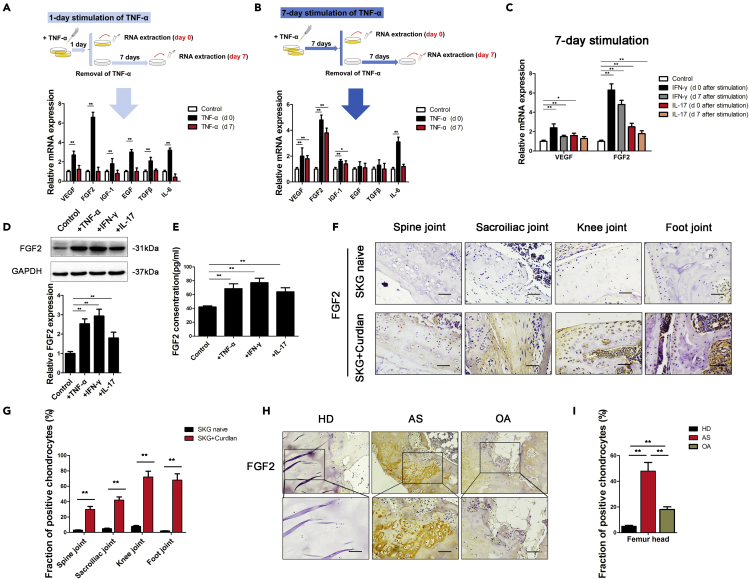
Figure 1.
Seven-day stimulation with inflammatory factors increased FGF2 expression in chondrocytes
(A and B) Diagram of 2 different modes of TNF-α stimulation on chondrocytes. The expression of angiogenic factors (VEGF, FGF2, IGF-1, EGF, TGF-β, and IL-6) was measured in chondrocytes cultured with TNF-α for 1 day (A) or 7 days (B).
(C) qRT-PCR analysis of VEGF and FGF2 expression in chondrocytes cultured with IFN-γ or IL-17 for 7 days, followed by the removal of the stimulus for 0 days or 7 days, respectively.
(D and E) FGF2 expression was measured by WB (D) and ELISA (E) in chondrocytes cultured with TNF-α, IFN-γ, or IL-17 for 7 days.
(F) IHC analysis of FGF2 protein in the spine joint, sacroiliac joint, knee joint and foot joint of SKG mice. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(G) Quantification of the proportions of FGF2-positive chondrocytes in SKG mice (n = 10 mice per group).
(H) IHC analysis of FGF2 protein in femur heads of healthy donors (HD), ankylosing spondylitis patients (AS) and osteoarthritis patients (OA). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(I) Quantification of the proportions of FGF2-positive chondrocytes in femur heads. (n = 10 people per group). Bars show the means ± SD.
∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01, 2-tailed Student's t-test (A, B, C, D, E, and G) and one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test (I). d0 = day 0; d7 = day 7; HD = healthy donors; AS = ankylosing spondylitis; OA = osteoarthritis.