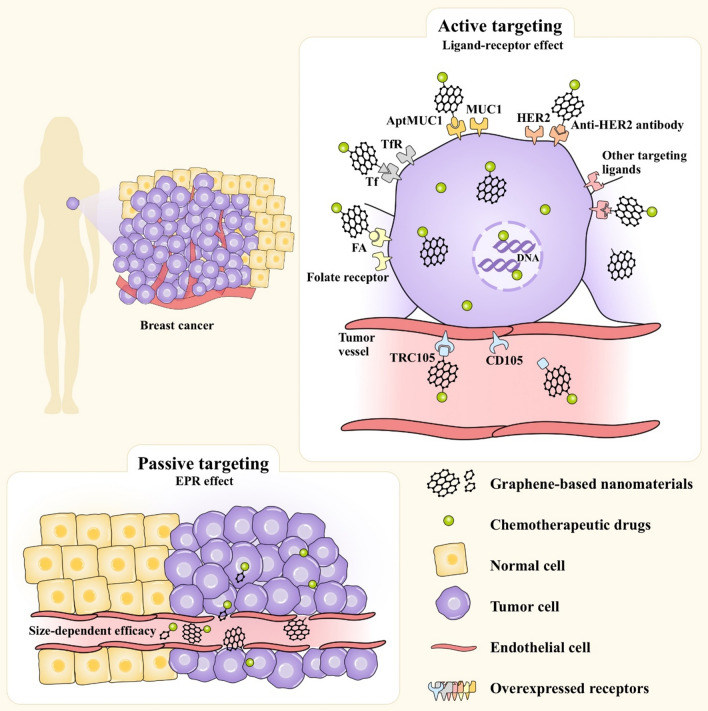
Fig. 2.
Schematic illustrations of active and passive GBN targeting. Targeting ligands on GBNs are directly attached to a site-specific receptor that is overexpressed on the surface of breast cancer cells or tumor vessels, and the targeting effects of GBNs are then achieved by utilizing receptor-mediated endocytosis and the EPR effect. Abbreviations: FA, folic acid; Tf, transferrin; TfR, Tf receptor; AptMUC1, MUC1-binding aptamer; TRC105, monoclonal antibody that binds CD105; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; EPR, enhanced permeability and retention