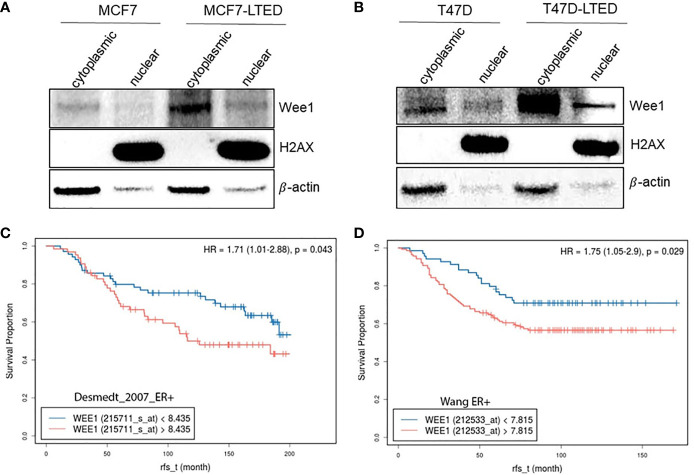
Figure 10.
Increased WEE1 correlates with survival of LTED cells and with poor prognosis in breast cancer. (A, B) Protein samples from MCF7 and T47D and their LTED derivatives (MCF7-LTED and T47D-LTED) were collected under basal conditions and fractionated to nuclear or cytoplasmic fractions and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Increased WEE1 protein levels was detected in both cytoplasm or nuclei of MCF7-LTED cells compared with the corresponding fractions in MCF7 cells. Similarly, in T47D-LTED cells, WEE1 protein levels were increased in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions compared with the corresponding fractions in T47D cells. Total H2AX (nuclear fractions) and β-actin (cytosolic fractions) were used as controls. Blot represents one of three independent experiments. (C, D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves was generated using two databases (GSE2034; n=134, GSE7390; n=209). Higher WEE1 gene expression (red) correlated with reduced relapse free survival (rfs) compared with low WEE1 gene expression (blue).