Figure 6.
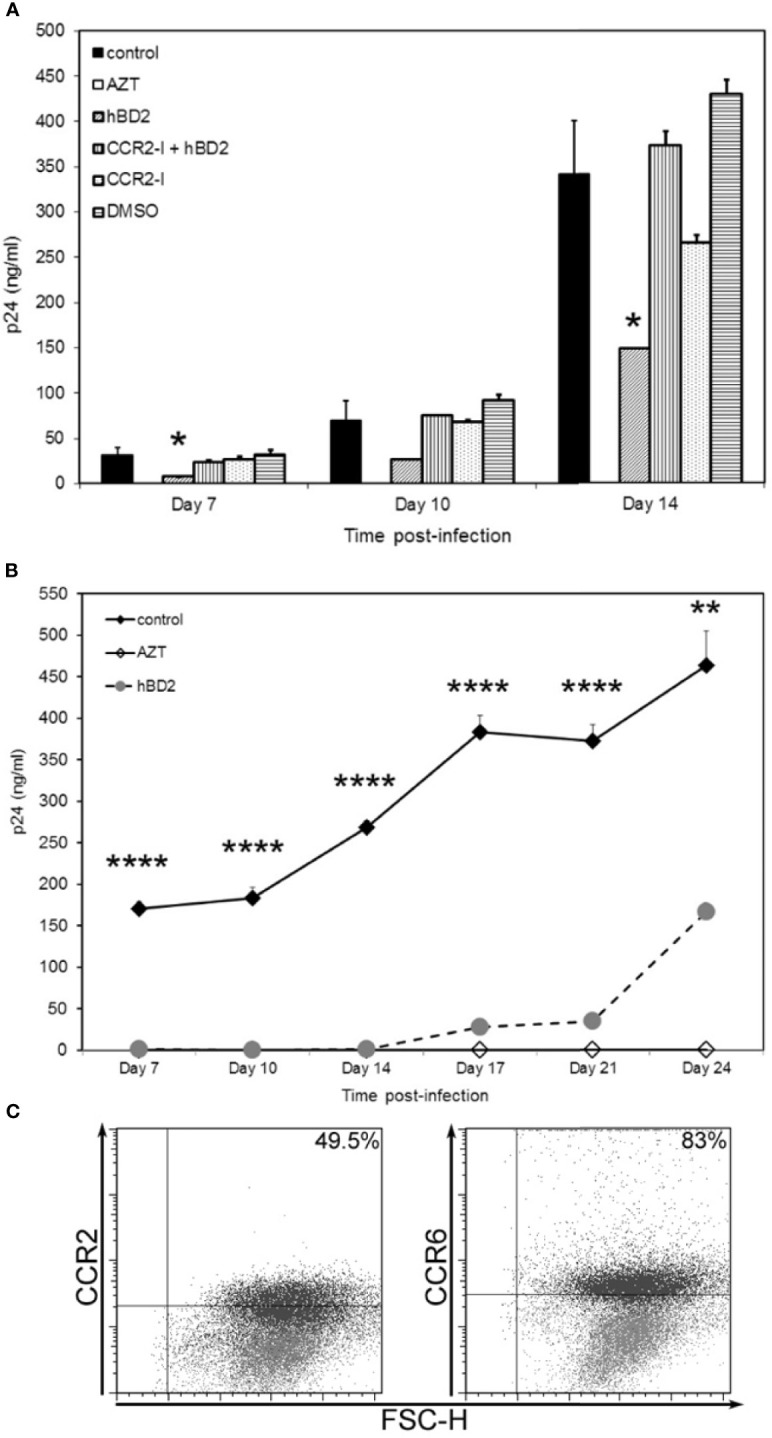
hBD2 can signal via more than one receptor type on macrophages. (A) Neutralization of CCR2 rescues HIV-1 infection. MDM were infected with HIV-1BaL. Cells were pretreated with AZT as control. Post-infection, infected untreated cells were pretreated with pharmacological antagonist RS102895 or DMSO control for 2 hrs followed by culture in presence or absence of hBD2 to the cultures. Infection was monitored by assaying supernatants for HIV p24 production by ELISA at the times indicated. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of triplicates. *P < 0.05 between treatment and control infection determined with unpaired two-tailed t test. Representative experiment, n=2. (B) hBD2 signals via an as yet unidentified receptor. MDM, that were CCR2- CCR6- (by FACS staining), prior to start of infection, were infected with HIV-1BaL. Cells were pretreated with AZT as control. Post-infection, cells were cultured in presence or absence of hBD2. Infection was monitored by p24 ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of triplicates. **P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0001 between treatment and control infection determined with unpaired two-tailed t test. (C) CCR2 and CCR6 surface expression levels vary with time. Uninfected, untreated cells from the donor used in (B) were harvested and stained for flow cytometry analysis as described in Materials and Methods. Data analyzed using FlowJo software. Forward scatter dot plots show the fluorescence and percentage of cells positive for CCR2 and CCR6 at Day 0 (grey) and Day 23 (black) as compared to the respective isotype-matched controls.
