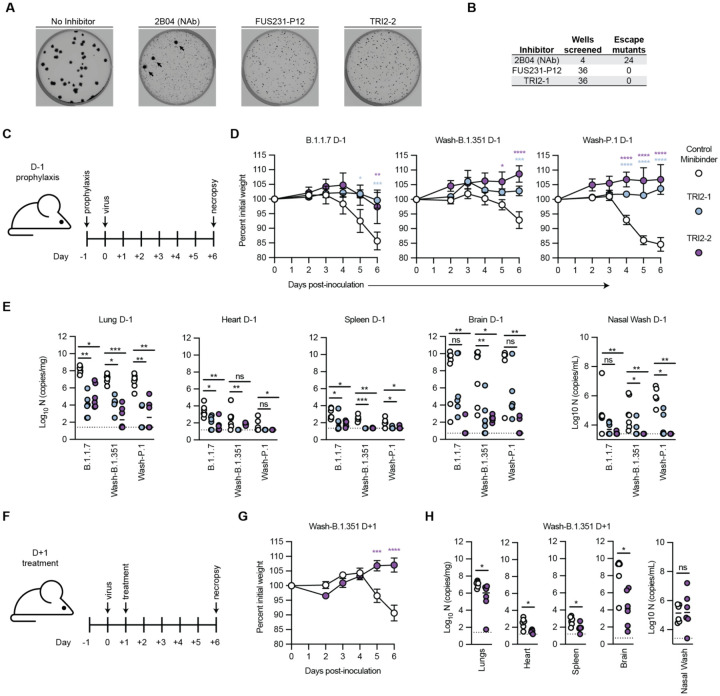
Fig. 5. Top multivalent minibinder candidates are escape resistant and protect mice from SARS-CoV-2 infection via pre- and post-exposure intranasal administration.
(A) Plaque assays were performed to isolate VSV-SARS-CoV-2 chimera virus escape mutants against a control neutralizing antibody (2B04) and the FUS231-P12 and TRI2–2 multivalent minibinders. Images are representative of 36 replicate wells per multivalent minibinder. Large plaques, highlighted by black arrows, are indicative of escape. (B) Table summarizing the results of the viral escape screen. (C-E) K18-hACE2-transgenic mice (n = 6/timepoint) were dosed with 50 μg of the indicated minibinder by i.n. administration (50 μl total) 24 h prior (D-1) to infection with 103 focus forming units of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.1.7, Wash-B.1.351, or Wash-P.1 i.n. on Day 0. (D) Daily weight-change following inoculation (mean ± SEM; n = 6, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test: * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001). (E) At 6 days post infection (6 dpi) animals (n = 6/timepoint) were sacrificed and analyzed for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA by RT-qPCR in the lung, heart, spleen, brain, or nasal wash (n = 6: Kruskal-Wallis test: ns, not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001). (F-H) K18-hACE2-transgenic mice (n = 6/timepoint) were dosed with 50 μg of the indicated minibinder by i.n. administration (50 μl total) 24 h after (D+1) infection with 103 focus forming units of the SARS-CoV-2 Wash-B.1.351 variant on Day 0. (G) Daily weight-change following inoculation (mean ± SEM; n = 6, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test: * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001). (H) At 6 dpi, animals (n = 6/timepoint) were sacrificed and analyzed for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA by RT-qPCR in the lung, heart, spleen, brain, or nasal wash (n = 6: Mann-Whitney test: ns, not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001).