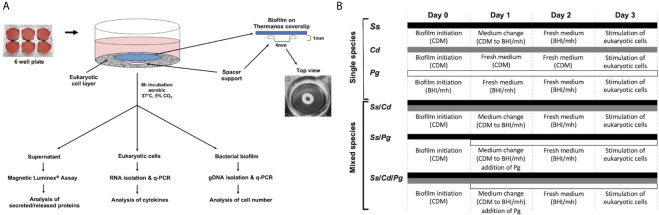
Figure 1.
Experimental set-up for bacterial biofilm formation and its interaction with oral mucosal and gingival cells. (A) Oral epithelial cells were grown in 6-well plates and challenged with bacterial biofilms that were separately grown on Thermanox coverslips. Mature biofilms were developed and incubated with medium changes every 24 h for 72 h. The coverslips were carefully placed with the biofilm facing toward the epithelial cells on a spacer which forms a gap of approximately 1 mm. Subsequently, the cells were incubated for 6 h. To determine the expression of IL-6 and IL-8 with q-PCR as well as the abundance of selected immune markers with Magnetic Luminex® Assay, the supernatants and the eukaryotic cells were collected and processed as described in the Materials and Methods. Biofilm cells were collected to determine the number and composition of the biofilms with q-PCR. (B) Thermanox cover slips were inoculated with bacteria from single species pre-cultures as described in Material and Methods at d 0. After 24 h (d 1), the growth medium was changed. For biofilms containing P. gingivalis, the species was added as indicated on day 1. After 48 h (d 2), the medium was changed, and at 72 h (d 3), biofilms were used for stimulating the eukaryotic cells. Different bars indicate the presence of respective species at the corresponding time points. CDM, chemical defined medium; BHI/mh, brain heart infusion supplemented with menadione (5µg/ml) and hemin (1µg/ml); Ss, S. sanguinis SK36, Cd, C durum JJ1, Pg, P. gingivalis ATCC33277.