Figure 4.
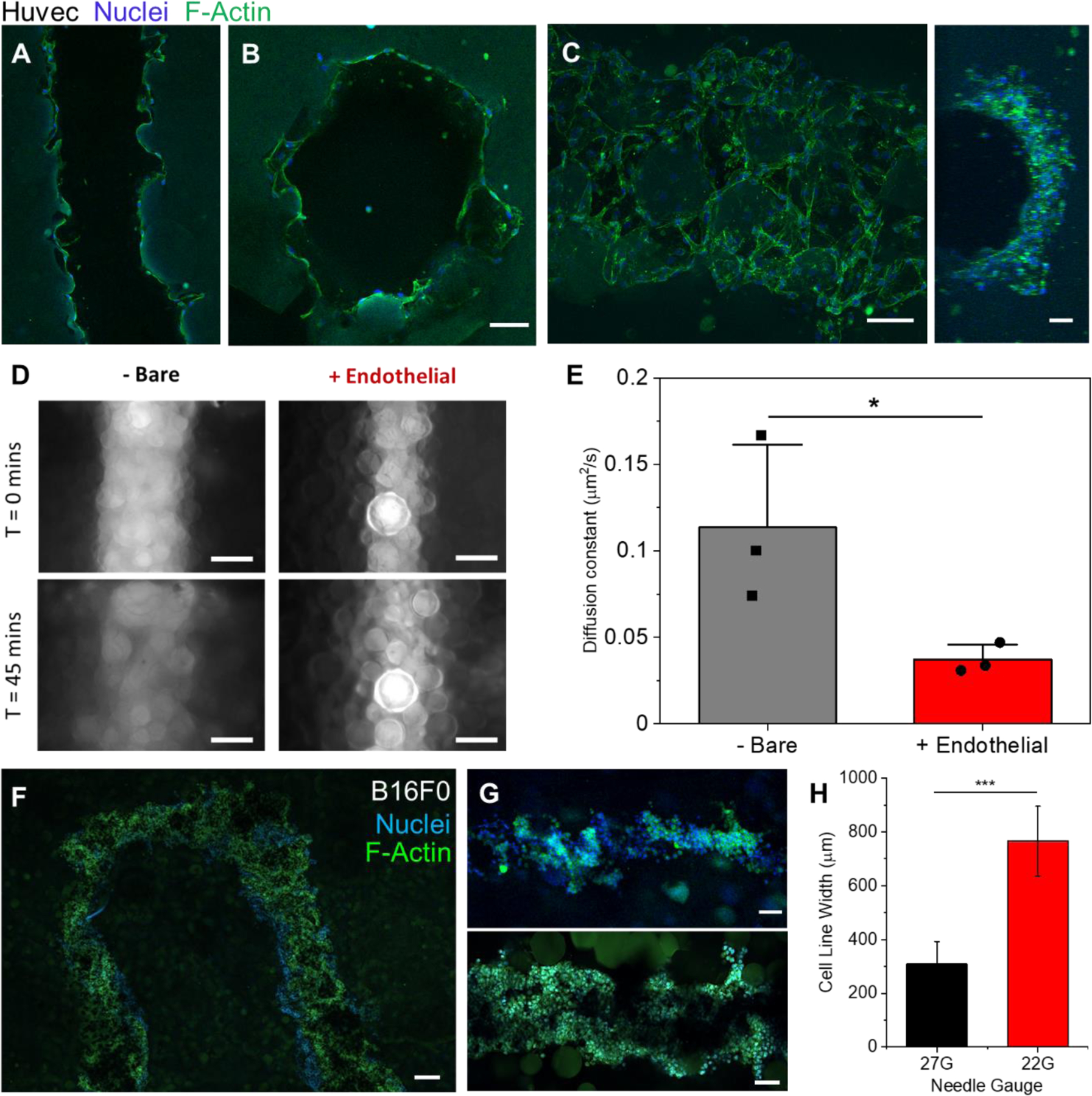
Vascular cell seeding and cancer cell printing. A) Confocal plane of Huvec cells seeded along the walls of a printed channel after 5 days. B) A cross section confocal image of the same gel to verify endothelial cells along the entire channel circumference. C) A max intensity z-stack projection (left, ImageJ) of the top half of a channel of endothelial cells after 5 days (Huvecs) along with a 3D projection image of the side view of that channel (right). D) Epifluorescence images taken of 40kDa FITC-Dextrans in cell-free (left images) and cell laden (right images) vascular channels at the times of 0 (top) and 45 minutes (bottom). E) Plot of calculated diffusion coefficients of 40kDa Dextrans in cell laden and cell free vasculature channels (n=3, P<0.05). F) Confocal image of the top (z-plane) of a U print of a fluidized cell pellet (B16F0). G) Confocal images of printed tumor lines (B16F0) from a 27G needle (Top) and 22G needle (Bottom). H) Plot of the measured average width of tumor line prints from 22G and 27G needles (n=6, P<0.001). Scale bars: 100µm (A, B, C, G), 200μm (D, F)
