Figure 7.
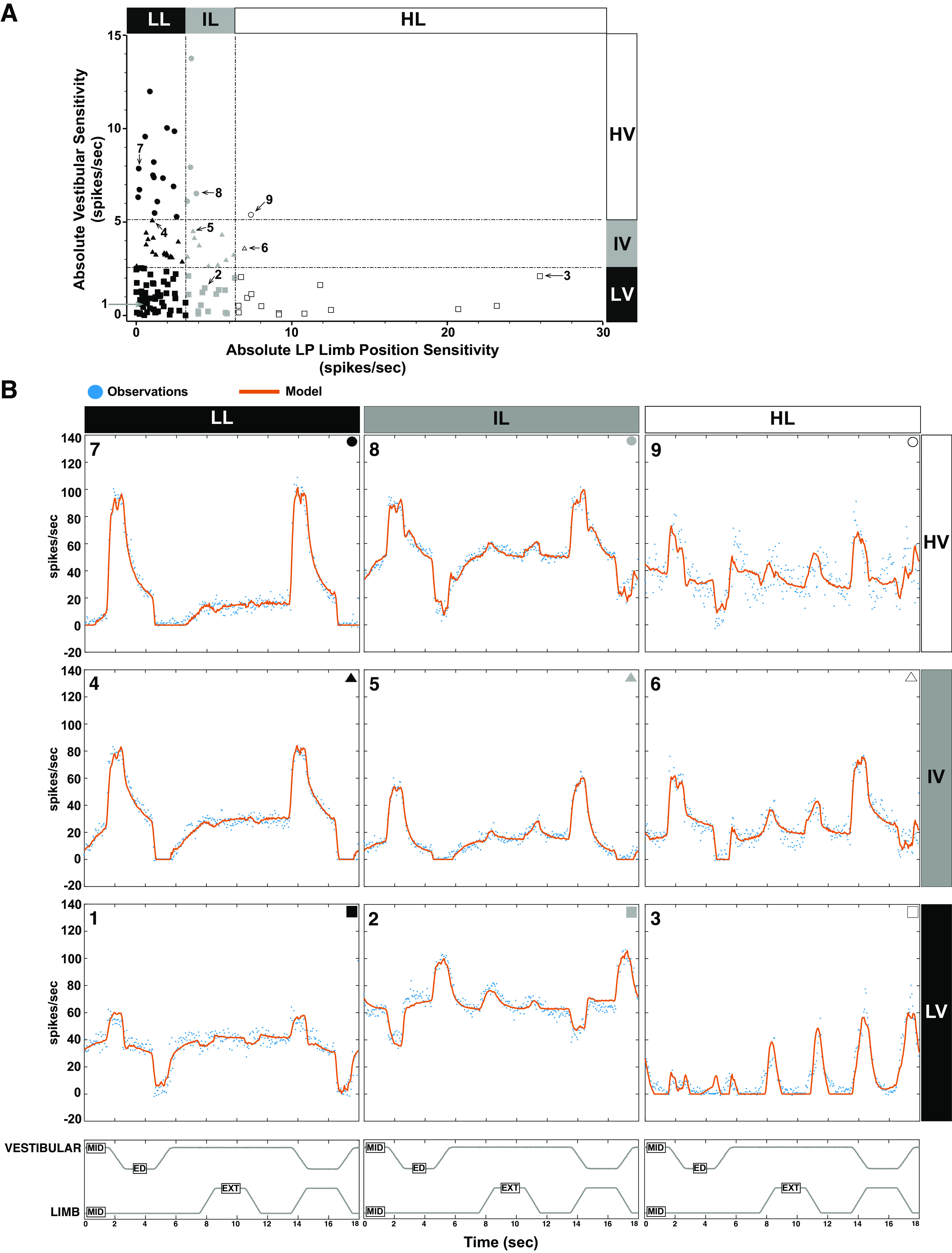
A: neurons could be further divided into nine groups on the basis of vestibular and low pass limb position sensitivities. Units labeled 1 through 9 correspond to the example units shown in B. B: the averaged responses of nine units represent the salient features of vestibular nucleus (VN) neuron responses to combined vestibular and hindlimb stimulation. The observed firing rate (blue dots) and the modeled firing rate (the fit of the model to the data; orange solid line, see Iterative Modeling Strategy for Vestibular and Limb Signal Identification) are shown for each unit. 7–9: units classified as having high absolute vestibular sensitivity; 4–6: units have intermediate absolute vestibular sensitivity; 1–3: units have low absolute vestibular sensitivity. Units 1, 4, and 7 have low absolute LP limb position sensitivity, units 2, 5, and 8 have intermediate absolute LP limb position sensitivity, whereas units 3, 6, and 9 have high absolute LP limb position sensitivity. ED, ear down; EXT, extension; HL, high limb; HV, high vestibular; IL, intermediate limb; IV, intermediate vestibular; LL, low limb; LP, low pass; LV, low vestibular; MID, midline.
