FIGURE 3.
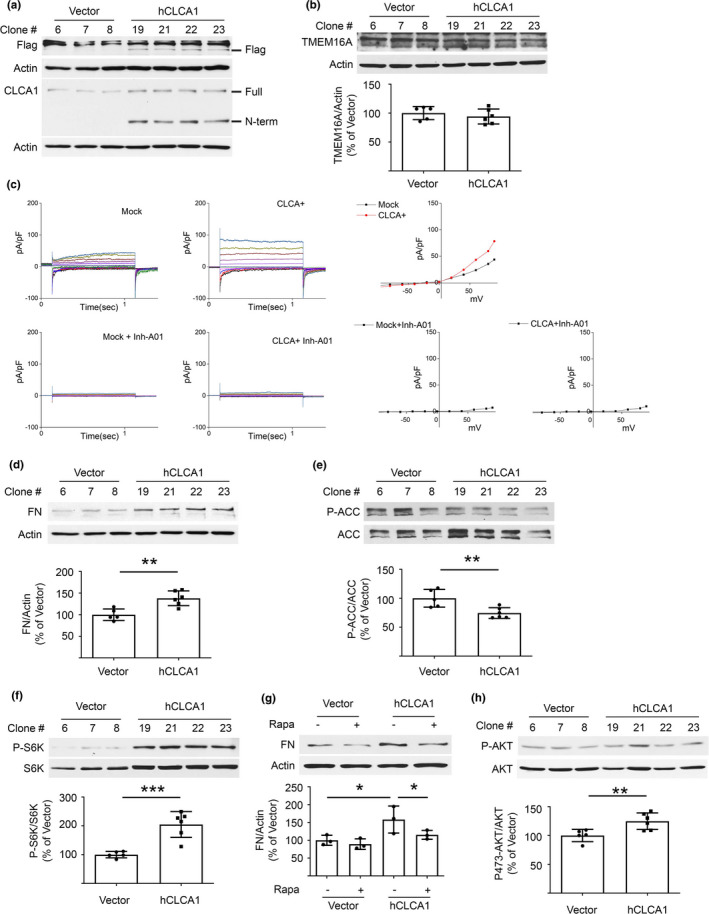
Overexpression of hCLCA1 increases matrix protein and induces changes in signaling kinases in proximal tubular epithelial cells in vitro. (a) Immunoblotting shows increased CLCA1 expression (130 kDa) and probably of its N‐terminal fragment (72 kDa) in cells stably transfected with hCLCA1 (six clones) versus control plasmid transfected clones (five clones); bands from three control and four hCLCA1 overexpressing clones are shown. (b) hCLCA1 overexpression did not alter TMEM16A expression. (c) Whole cell patch‐clamp shows an increase in Cl− current in hCLCA1 overexpressing cells versus vector‐transfected controls (mock). Cl− current was abolished by T16Ainh‐A01 in both mock and hCLCA1 overexpressing cells. (d) Overexpression of hCLCA1 resulted in increase in matrix protein fibronectin (FN). (e, f). Immunoblotting with specific antibodies showed decrease in ACC phosphorylation, and increase in p70S6 kinase (S6K) phosphorylation. (g) Incubation with 25 nM rapamycin for 30 min abolished the increase in fibronectin expression seen following overexpression of hCLCA1 (data from three experiments are shown). (h) Overexpression of hCLCA1 increased Akt phosphorylation at Ser473. Data (mean ± SD) are shown in bars in scatter plots and were analyzed by t test (b, d‐f, and h) or ANOVA (g). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (d, e, f, h) employed five control and six hCLCA1 clones.
